Introduction:
In the realm of global finance, the exchange rate between currencies is a critical factor that shapes international trade, investment, and travel. Among the numerous currency pairs, the exchange rate between the Indian Rupee (INR) and the United States Dollar (USD) holds immense significance. This article delves into the intricacies of the INR to USD forex rate, offering an in-depth understanding of its dynamics, influencing factors, and implications.
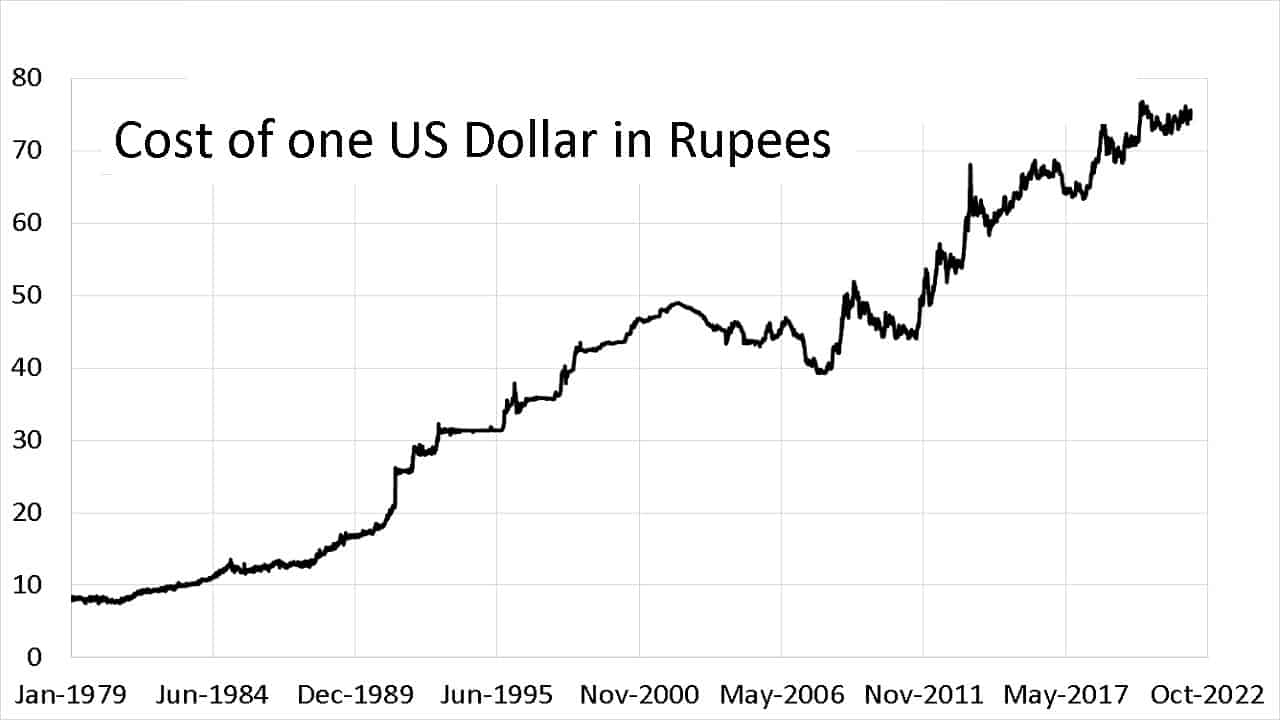
Image: freefincal.com
Understanding the INR to USD Forex Rate:
The INR to USD forex rate refers to the number of Indian Rupees (INR) required to purchase one United States Dollar (USD). This exchange rate is constantly fluctuating due to a multitude of economic and political factors. Thus, staying abreast of the latest INR to USD forex rate is crucial for individuals and businesses engaged in international transactions.
Historical Perspective:
The INR to USD exchange rate has witnessed significant fluctuations over the years, shaped by India’s economic policies, global economic conditions, and geopolitical events. From its inception in 1947, the INR to USD rate has ranged from approximately 7.5 to 120 INR per USD. Notably, economic liberalization in India during the 1990s led to a marked depreciation of the INR, aligning it more closely with market forces.
Influencing Factors:
The INR to USD forex rate is influenced by a complex interplay of domestic and international factors. Key among them are:
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates in India and the United States can impact the movement of capital and influence the exchange rate. Higher interest rates in India, for instance, can attract foreign capital and strengthen the INR.
- Inflation: Differences in inflation rates between the two countries affect the purchasing power of both currencies and can influence the exchange rate. Higher inflation in India, for example, can weaken the INR against the USD.
- Economic Growth: The overall economic growth rate of India and the United States contributes to exchange rate fluctuations. Robust economic growth in India can boost the value of the INR, while slower growth can lead to its depreciation.
- Trade Balance: The difference between the value of goods and services exported and imported by India influences the INR to USD exchange rate. A surplus in trade favors the INR, while a deficit exerts downward pressure.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: India’s foreign exchange reserves, consisting of currencies and gold held by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), can influence the exchange rate. Higher reserves provide the RBI with greater flexibility to intervene in the foreign exchange market and stabilize the INR.
Implications:
The INR to USD forex rate has far-reaching implications for various stakeholders:
- Individuals: Tourists and individuals engaged in cross-border transactions are directly affected by the exchange rate. A stronger INR makes travel and purchases abroad more affordable, while a weaker INR increases the cost of these expenses.
- Businesses: Multinational corporations, exporters, and importers need to consider the exchange rate when planning their global operations. Changes in the exchange rate can affect their revenue, costs, and overall profitability.
- Government: The government plays a crucial role in managing the INR to USD exchange rate through monetary and fiscal policies. Stability in the exchange rate fosters economic growth and facilitates international trade.
Conclusion:
The INR to USD forex rate is a dynamic and ever-changing aspect of global finance. By understanding the factors that influence this rate and its implications, individuals, businesses, and governments can effectively manage their financial activities that involve cross-border transactions. Staying updated on the latest INR to USD forex rate is a key part of navigating the complexities of international exchange markets.

Image: yufyfiqec.web.fc2.com
Inr To Usd Forex Rate






