South Africa, an economic powerhouse on the African continent, plays a pivotal role in international trade. Its trade policies shape not only its domestic economy but also its standing in the global marketplace. Analyzing these policies is crucial for understanding the country’s economic trajectory and its relationship with other countries.
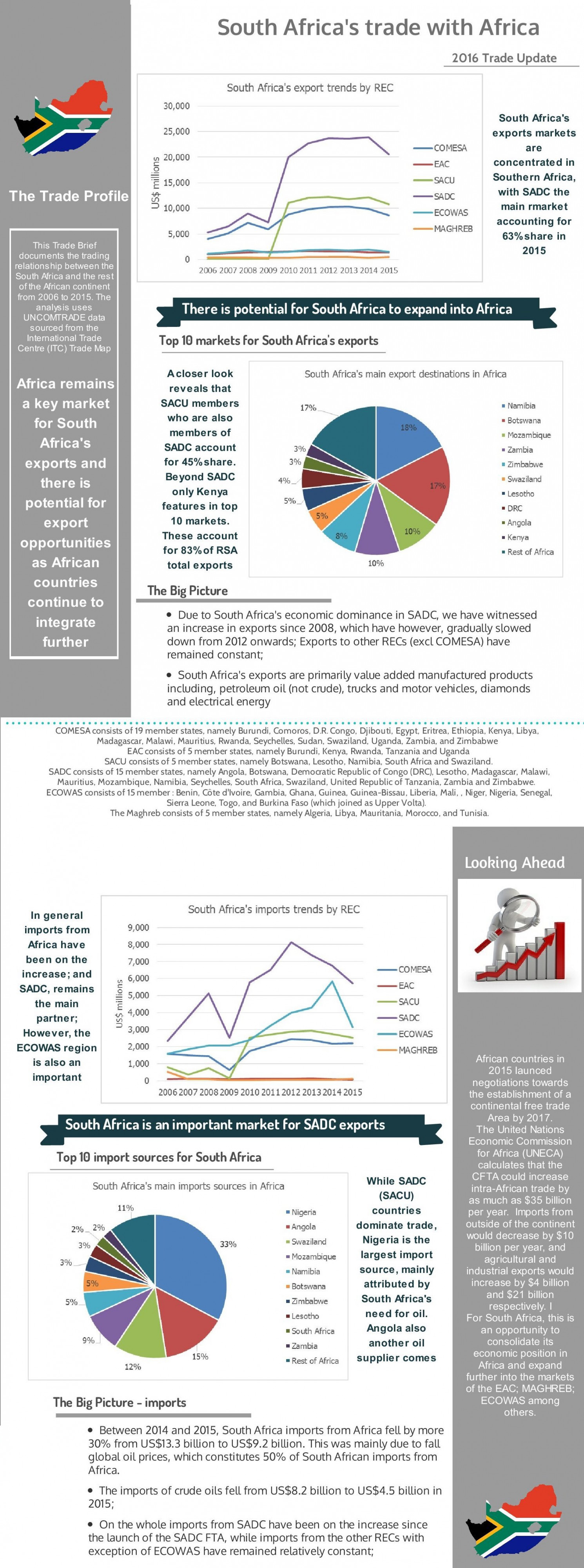
Image: www.tralac.org
South Africa’s trade policies have undergone significant evolution over the years. The country’s history of apartheid left a legacy of economic disparities and trade barriers. Post-apartheid, the government has strived to create a more equitable and inclusive economy, with trade policies playing a central role in this transformation.
Pillars of South Africa’s Trade Policies
South Africa’s trade policies are based on several fundamental pillars:
- Regional Integration: South Africa is an active member of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the African Union. Its trade policies prioritize strengthening economic ties within these regional blocs.
- Trade Diversification: South Africa seeks to reduce its dependence on traditional export markets. The government promotes trade with emerging economies in Asia, Latin America, and Eastern Europe.
- Value Addition: South Africa aims to move beyond raw material exports by focusing on value-added industries. Policies incentivize businesses to invest in local processing and manufacturing.
- Tariff Reform: The country has steadily reduced tariffs in line with its commitment to the World Trade Organization. However, it maintains some protective tariffs to safeguard key domestic industries.
- Intellectual Property Protection: South Africa recognizes the importance of intellectual property rights in promoting innovation and creativity. Its policies aim to strike a balance between protecting creators and fostering access to knowledge.
Benefits of South Africa’s Trade Policies
South Africa’s trade policies have brought about numerous benefits for the country:
- Economic Growth: Trade has been a major driver of South Africa’s economic growth. Increased exports boost revenue and create jobs.
- Job Creation: Expanding trade sectors create employment opportunities in various fields, including manufacturing, agriculture, and logistics.
- Increased Market Access: South Africa’s trade agreements with other countries have opened new markets for its businesses, allowing them to reach a wider customer base.
- Technology Transfer: Through trade, South Africa gains access to new technologies and expertise, which can enhance local production capabilities.
- Reduced Poverty: Trade can help alleviate poverty by creating income-generating opportunities and reducing the cost of essential goods.
Challenges of South Africa’s Trade Policies
While South Africa’s trade policies have brought benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
- Import Competition: Reduced tariffs can make it harder for domestic industries to compete with imported goods.
- Trade Deficits: South Africa often runs trade deficits, where imports exceed exports. This can put pressure on the country’s currency and foreign reserves.
- Inequality: Trade policies can exacerbate income inequality if benefits are not distributed equitably.
- Environmental Concerns: The focus on trade and economic growth can sometimes come at the expense of environmental protection.
- Political Uncertainty: Political instability and policy shifts can create uncertainty for businesses and disrupt trade.

Image: www.linkedin.com
Analysis Of South Africa’S Trade Policies
Conclusion
South Africa’s trade policies are a complex and dynamic aspect of the country’s economy. They have the potential to drive growth and prosperity, but they also pose challenges that need to be addressed. By understanding the pillars, benefits, and challenges of these policies, we can engage in informed discussions about their future direction. South Africa’s government, businesses, and citizens must work together to create a trade policy landscape that promotes economic development while addressing societal disparities and environmental concerns.






