In the tapestry of global history, the African gold trade left an indelible mark on the 16th century, transforming North Africa into a bustling hub of economic and cultural exchange. Situated at the crossroads of trade routes connecting sub-Saharan Africa with Europe and the Middle East, North African cities such as Timbuktu, Marrakech, and Algiers emerged as centers of commerce and wealth.

Image: www.johnogroat-journal.co.uk
The Wealth of the Nile and the Western Sudan
The vast and fertile lands of the Nile River Valley and the Western Sudan were the sources of abundant gold. The gold extracted from alluvial deposits and mines found its way into the hands of traders who would embark on arduous journeys across the Sahara Desert, connecting West Africa with North Africa.
Monarchs, Merchants, and Trans-Saharan Trade
The burgeoning gold trade caught the attention of powerful monarchs across North Africa. From the Atlas Mountains to the Nile Valley, rulers sought to control the flow of precious metal and establish trading alliances. Merchants from diverse backgrounds, from Berber nomads to Jewish traders, played a crucial role in facilitating the trans-Saharan gold trade network.
Exchange and Enrichment: Shaping North African Culture
The influx of gold significantly contributed to the economic prosperity of North African cities. The wealth generated not only spurred infrastructural development and architectural wonders but also cultivated a vibrant and cosmopolitan atmosphere. The gold trade fostered cultural exchange, as ideas, goods, and technologies traveled alongside the flow of precious metal.
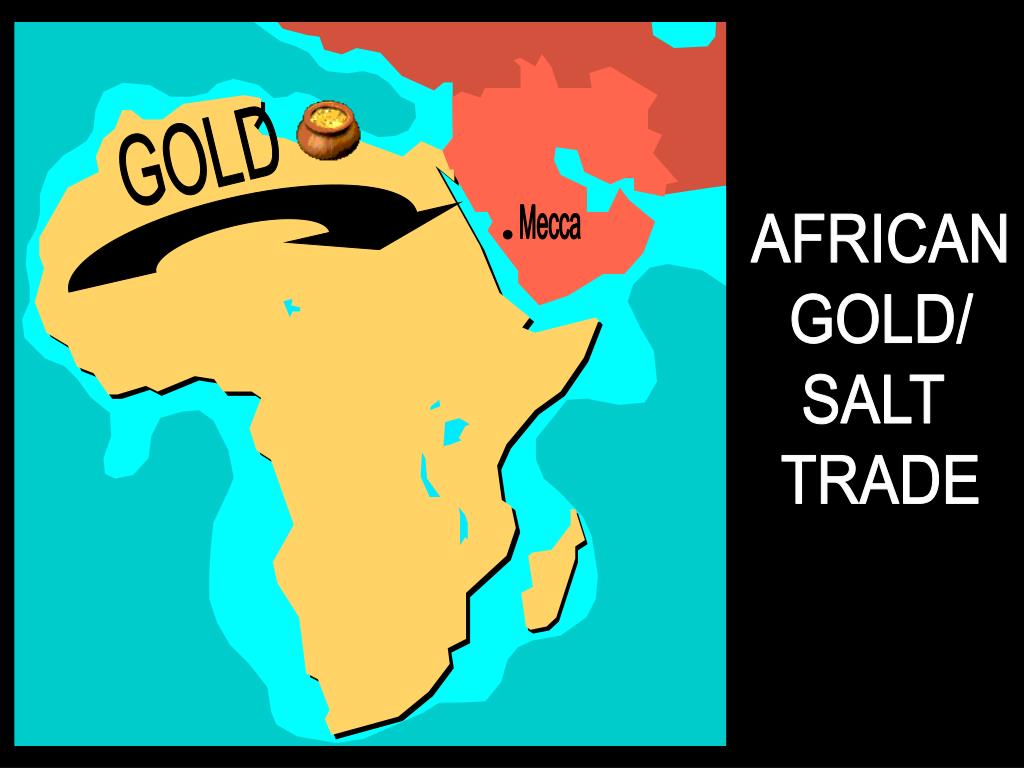
Image: www.slideserve.com
Mining and Exchange in the Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire, located in West Africa, played a pivotal role in the gold trade. The empire controlled the critical gold-producing region of Bambuk, solidifying its status as a major supplier of gold to North African markets. The Songhai’s prosperity and influence were closely intertwined with the gold trade, and the empire developed sophisticated mining techniques and trading networks.
Gold and the Portuguese Ascendency
In the late 15th century, the arrival of Portuguese explorers along the West African coast added a new dimension to the gold trade. The Portuguese established trading posts and sought to monopolize the lucrative gold trade. This competition between European powers and North African kingdoms shaped the dynamics of the gold trade in the 16th century.
Tips and Expert Advice: Impacts and Evolution of the Gold Trade
The African gold trade had a profound impact on the development of North Africa, West Africa, and Europe. Experts emphasize the following key points:
- Economic Transformation: The gold trade accelerated the economic development of both North and West Africa, leading to the rise of thriving cities and trading centers.
- Technological Diffusion: The movement of gold facilitated the exchange of technologies, such as mining techniques, architectural innovations, and navigation methods.
- Cultural Enrichment: The gold trade contributed to a vibrant exchange of ideas, beliefs, and cultural practices, leading to the synthesis of African and Islamic art and scholarship.
- Political Power: The control of gold trade routes and gold-producing regions played a significant role in determining political power and influence in North and West Africa.
FAQs on the African Gold Trade in North Africa
- Q: When did the trans-Saharan gold trade begin?
- Q: What was the primary use of gold in North Africa?
- Q: How did the Portuguese arrival impact the gold trade?
A: The trans-Saharan gold trade started in antiquity, with records indicating trade activities as early as the 8th century BC.
A: Gold was primarily used as a form of currency, fashioned into coins and traded for goods, services, and luxury items.
A: The Portuguese arrival introduced new players into the gold trade and increased competition for control of the trade routes.
African Gold Trade North Africa 16th Century
Conclusion: Echoes of a Golden Legacy
The African gold trade in North Africa during the 16th century left an enduring mark on the fortunes and destinies of both continents. The wealth, cultural exchange, and technological advancements that resulted from the gold trade shaped civilizations and societies, leaving a legacy that continues to echo in the sands of time. As we delve into this captivating chapter in history, let us appreciate the ingenuity, resilience, and global connections that emerged from the quest for this precious metal.
Are you intrigued by the complexities and fascinations of the African gold trade? If so, I encourage you to explore the vast tapestry of history, uncover hidden narratives, and engage with the enduring legacy of this remarkable chapter in human endeavor.






