The United States and Africa enjoy a robust trading relationship, with the exchange of goods and services playing a significant role in economic growth and development on both continents. In 2022 alone, the US traded approximately $57.3 billion worth of goods with Africa, solidifying the continent’s position as an important economic partner.
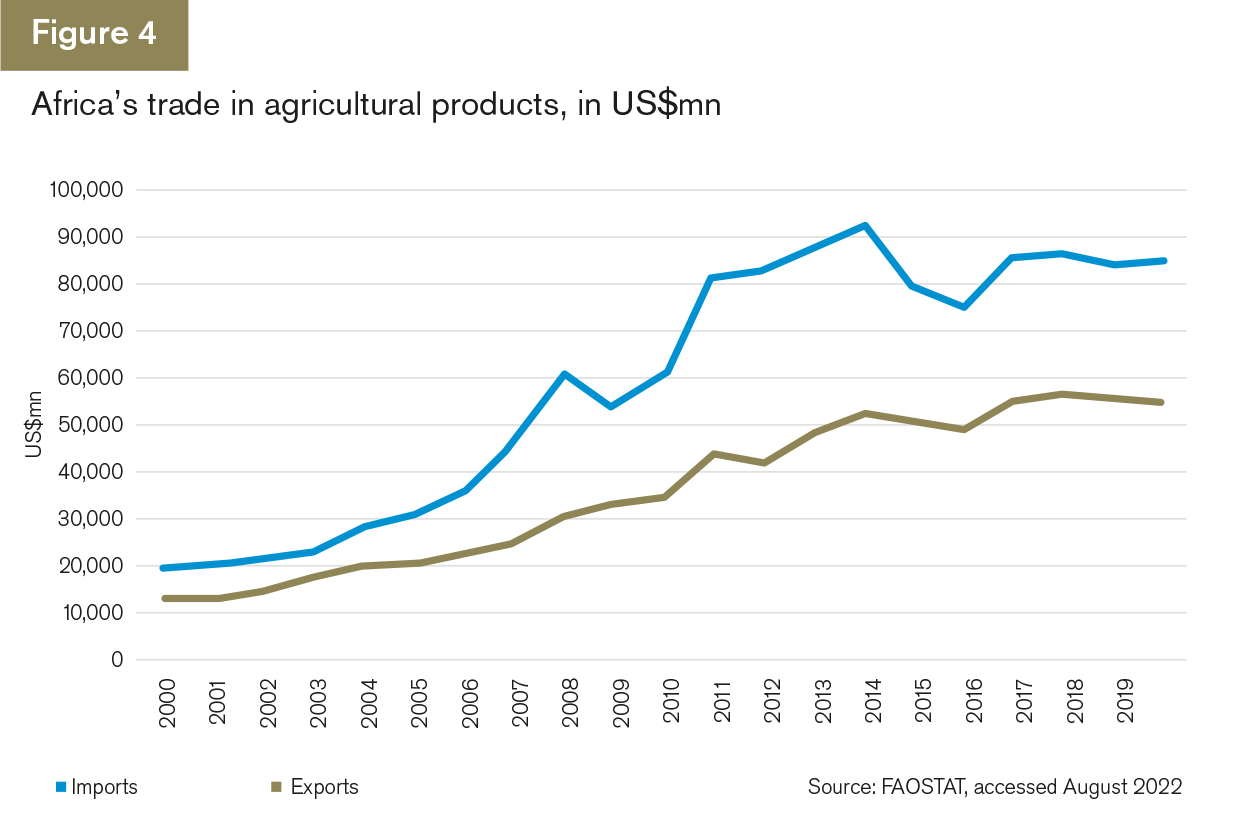
Image: www.gtreview.com
Delving into the numbers reveals fascinating insights into the nature of this trade relationship. The top US exports to Africa include transportation equipment, machinery, and agricultural commodities like wheat. In contrast, Africa’s exports to the US primarily comprise crude oil, minerals, and precious stones, reflecting the continent’s rich natural resources.
The benefits of this trade relationship are multifaceted. For the US, access to African markets provides opportunities for businesses to expand their global reach and foster economic growth. Simultaneously, for African nations, the influx of US goods and investments stimulates industrial development, creates jobs, and enhances living standards.
The trade relationship between the US and Africa has witnessed a steady upward trajectory in recent years, with both governments recognizing its importance. Numerous initiatives have been launched to further strengthen and expand this partnership, including the US African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
However, challenges remain in optimizing this trade relationship. Trade barriers, infrastructure constraints, and political instability in certain African countries continue to hinder the full realization of its potential. Addressing these challenges through cooperation and diplomacy will be crucial in unlocking the full benefits of the US-Africa trade relationship.
Unveiling the Top Trading Partners
Among African nations, Nigeria, South Africa, Angola, and Kenya stand as the leading trading partners for the United States. Nigeria, Africa’s largest economy, is a major consumer of US goods and services, particularly in the energy and transportation sectors. South Africa, with its advanced infrastructure and business-friendly environment, serves as a gateway for US companies entering African markets.
On the other hand, Angola, rich in natural resources, has emerged as a significant supplier of crude oil to the United States. Kenya, with its strategic location on the east coast of Africa, has become a hub for trade and investment, particularly in sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and renewable energy.
Beyond Bilateral Trade: Regional Integration and Investment
While bilateral trade remains a cornerstone of the US-Africa relationship, recent years have witnessed a growing emphasis on regional integration and investment. The establishment of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) in 2018 has ushered in a new era of economic cooperation and reduced trade barriers within Africa. This landmark initiative has the potential to create a continental market of over 1.3 billion people and boost intra-African trade.
Complementing trade, foreign direct investment (FDI) is another vital aspect of the US-Africa economic relationship. US companies have made significant investments across various sectors in Africa, from energy and infrastructure to manufacturing and telecommunications. This investment plays a crucial role in unlocking Africa’s economic potential, creating jobs, and fostering sustainable development.
Addressing Challenges and Fostering Sustainable Growth
Despite the positive strides made in US-Africa trade, challenges persist that could hinder its full potential. These include trade barriers such as tariffs and non-tariff measures, which can impede the free flow of goods and services. Addressing these barriers through negotiation and engagement will be vital in maximizing the benefits of trade.
Moreover, infrastructure constraints, particularly in energy, transportation, and ICT, pose challenges to trade and economic development in Africa. Significant investments are required to upgrade infrastructure and facilitate seamless connectivity across the continent.
Political instability and conflict in certain African countries also have detrimental effects on trade and investment. Promoting peace, stability, and good governance is essential for creating a conducive environment for economic growth and trade.

Image: www.researchgate.net
Us Africa Trade Statistics
Conclusion
The US-Africa trade relationship is a significant and dynamic component of global economic connections. With its vast potential for growth and development, this partnership can create a mutually beneficial future for both continents. By addressing challenges, fostering regional integration, and promoting sustainable development, the United States and Africa can unlock the full potential of their economic relationship and shape a brighter tomorrow for both.






