Money and Trade: The Foundation of Economies
Money, a medium of exchange, has played a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscapes of nations. Trade, the exchange of goods and services, has fostered interdependence and spurred economic growth. South Africa, with its rich history and diverse cultures, provides a fascinating lens through which to explore the evolution of money and trade.
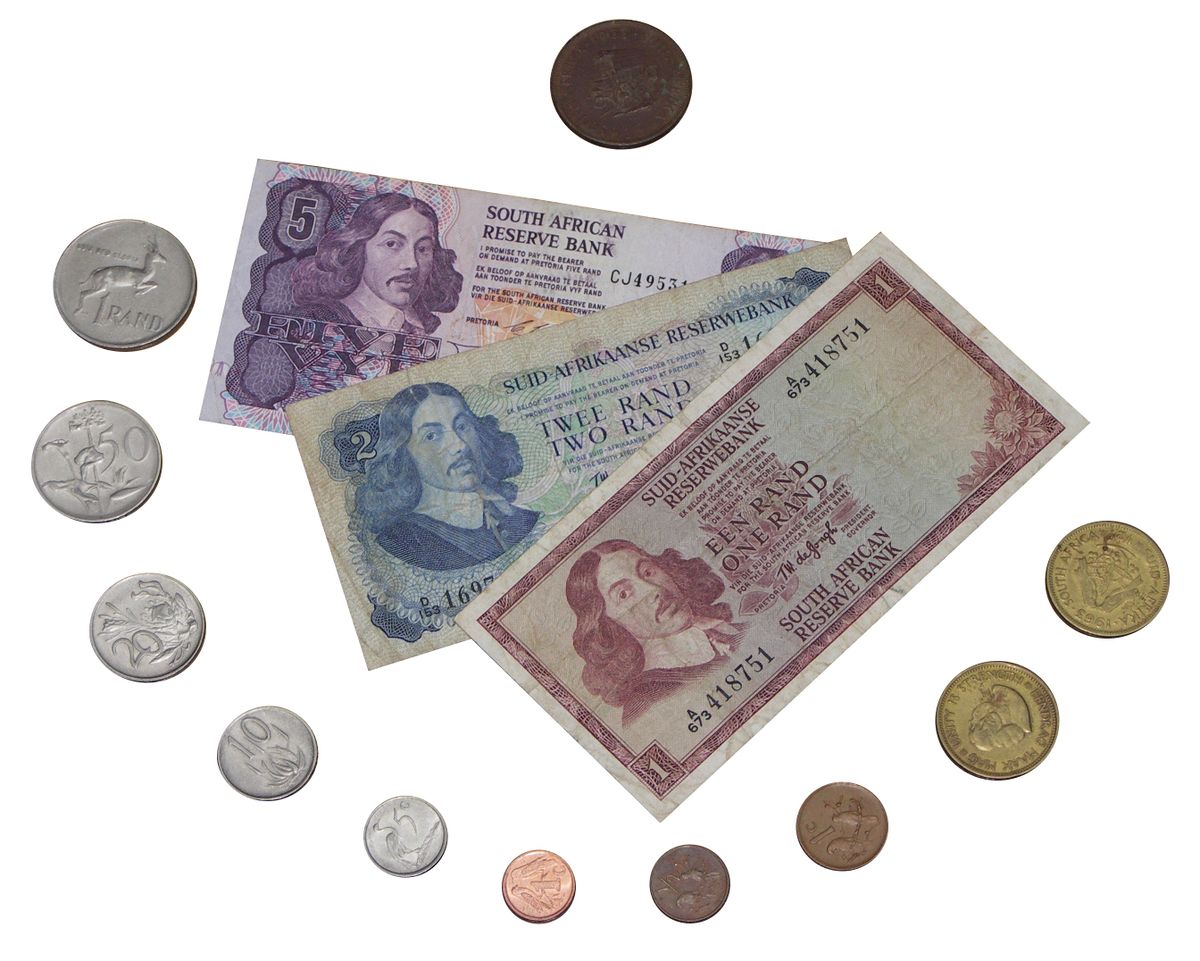

Image: www.marefa.org
The Birth of Money in South Africa
The earliest forms of money in South Africa emerged during the pre-colonial era. Cattle, known as “imfuyo,” served as a form of wealth and a means of exchange among pastoralist communities. As societies grew more complex, beadwork, iron, copper, and shells gained monetary value.
Colonial Currency and the Rise of Trade
The arrival of European settlers in the 17th century introduced new forms of currency, including Spanish coins known as “rials.” These coins facilitated trade between European traders and local merchants. The Dutch East India Company, which established Cape Town as a refreshment station, minted its own currency, the “rijksdaalder,” to regulate trade in the Cape Colony.
The Emergence of Formal Currency
In the 19th century, as the British established control over South Africa, they introduced the pound sterling as the official currency. The discovery of diamonds and gold in the late 1800s led to a rapid expansion of trade and spurred the establishment of banks and financial institutions.
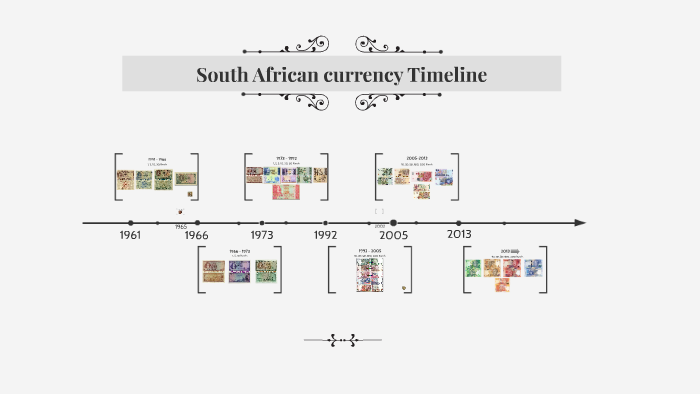
Image: www.psdtolive.com
The Apartheid Era and Economic Inequality
The apartheid era (1948-1994) had a significant impact on money and trade in South Africa. The implementation of separate economic systems for white and black citizens created vast disparities in wealth and opportunities. The Rand, introduced as the national currency in 1961, mirrored these inequalities, with the value of black wages significantly lower than that of white wages.
Post-Apartheid Transitions and Economic Progress
The end of apartheid in 1994 marked a new chapter in the economic history of South Africa. The introduction of democratic elections and the removal of economic barriers led to increased trade and foreign investment. The rand gained in stability, and the economy began to grow.
South Africa’s Place in the Global Economy
Today, South Africa is a major player in the global economy. It has a diversified economy that includes mining, manufacturing, agriculture, and services. Trade continues to play a vital role, with the country exporting minerals, agricultural products, and manufactured goods.
Expert Advice for Optimizing Your Economic Impact
- Embrace Digital Currency: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin offer new opportunities for cross-border trade and reduce transaction costs.
- Participate in Trade Agreements: Regional trade agreements, such as the Southern African Customs Union, facilitate seamless trade and access to new markets.
- Invest in Skills Training: A skilled workforce is essential for economic growth and competitiveness in global markets.
FAQs about Money and Trade in South Africa
Q: What was the first form of money used in South Africa?
A: Cattle served as a form of wealth and exchange among pre-colonial communities.
Q: How did apartheid impact the financial system?
A: Apartheid created separate economic systems for white and black citizens, resulting in vast wealth disparities and an undervalued black currency.
Q: What is South Africa’s main export commodity?
A: South Africa is a major exporter of minerals, including gold, diamonds, and platinum.
The History Of Money And Trade In South Africa
Conclusion
The history of money and trade in South Africa is a testament to the power of economics to shape societies. From the humble beginnings of cattle as currency to the globalized economy, South Africa’s journey provides valuable lessons about the importance of fostering inclusive growth and harnessing the potential of trade.
Call to Action: If you’re interested in learning more about the fascinating world of money and trade in South Africa, explore the resources available online. You can discover the intricate details of its history, its current impact, and its prospects for the future.






