Before the European slave trade, Africa had a long and complex history of slavery. Slavery varied greatly across different regions and time periods. However in many cases, it was an integral part of the economic and social fabric of society.
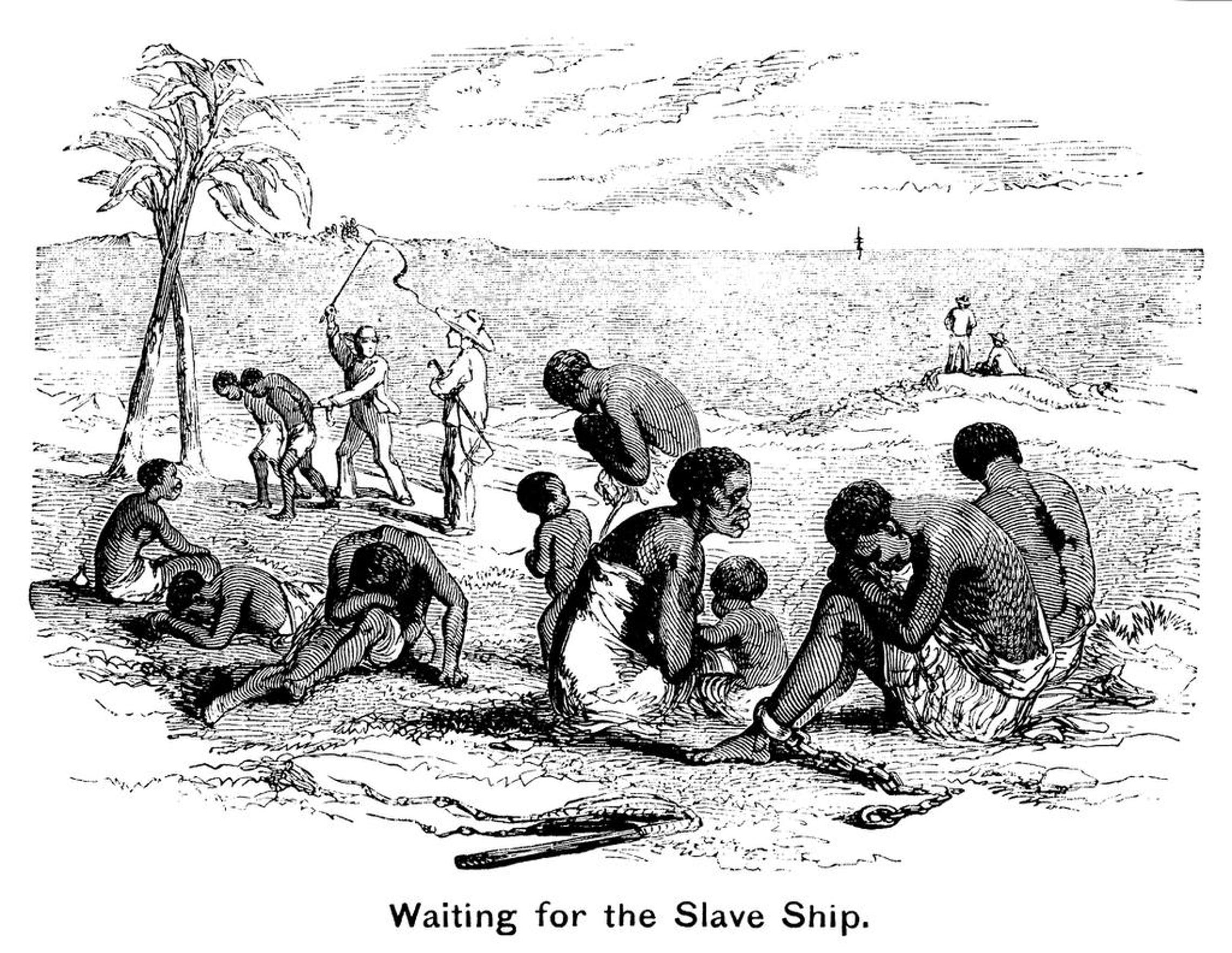

Image: deritszalkmaar.nl
Before the Transatlantic Slave Trade
During the period of the transatlantic slave trade, an estimated 12 million Africans were forcibly taken from their homes and enslaved in the Americas. The beginning of the transatlantic slave trade in the 15th century brought a shift in the nature of slavery in Africa. This marked the beginning of a brutal and dehumanizing system that would leave a lasting legacy on the continent for centuries to come.
In some regions, slaves were captured in warfare or through raids. In other areas, people were sold into slavery by their own families or communities. Slaves were often used as laborers in agriculture, mining, or domestic service and they were subjected to harsh treatment and abuse.
The impact of European colonialism played another key factor that shaped the history and patterns of slavery in Africa. As Europeans gained control over various regions, they altered existing forms of slavery, and intensified the practice of chattel slavery, where individuals were viewed as property that could be bought, sold and inherited.
Forms of Slavery
There were various forms of slavery in Africa that existed before the transatlantic slave trade. Here are key examples:
- Chattel Slavery: In its most extreme form, enslaved people were treated as property or chattel. They had no legal rights and could be bought, sold, or traded like any other commodity.
- Pledge Slavery: Individuals were enslaved as a form of collateral for debts or compensation for crimes committed by themselves or their family members.
- Domestic Slavery: Slaves worked within households, performing various duties and serving the needs of their owners’ families.
- Pawns or Security Slavery: People were temporarily handed over as security against debts or obligations and could be redeemed once the debt was repaid.
Abolition and Transition
Recognizing the inherent cruelty and injustice of slavery, global efforts and movements emerged to abolish slavery from the 18th century onwards. Driven by humanitarians, activists and abolitionists, the fight to eradicate slavery gained momentum.
In many African societies, the abolition of slavery led to significant social and economic changes and adaptations. Former slaves sought freedom and new opportunities while slave owners had to adjust to new labor systems. Some former slaves successfully integrated into society, pursued education, and even rose to positions of influence.
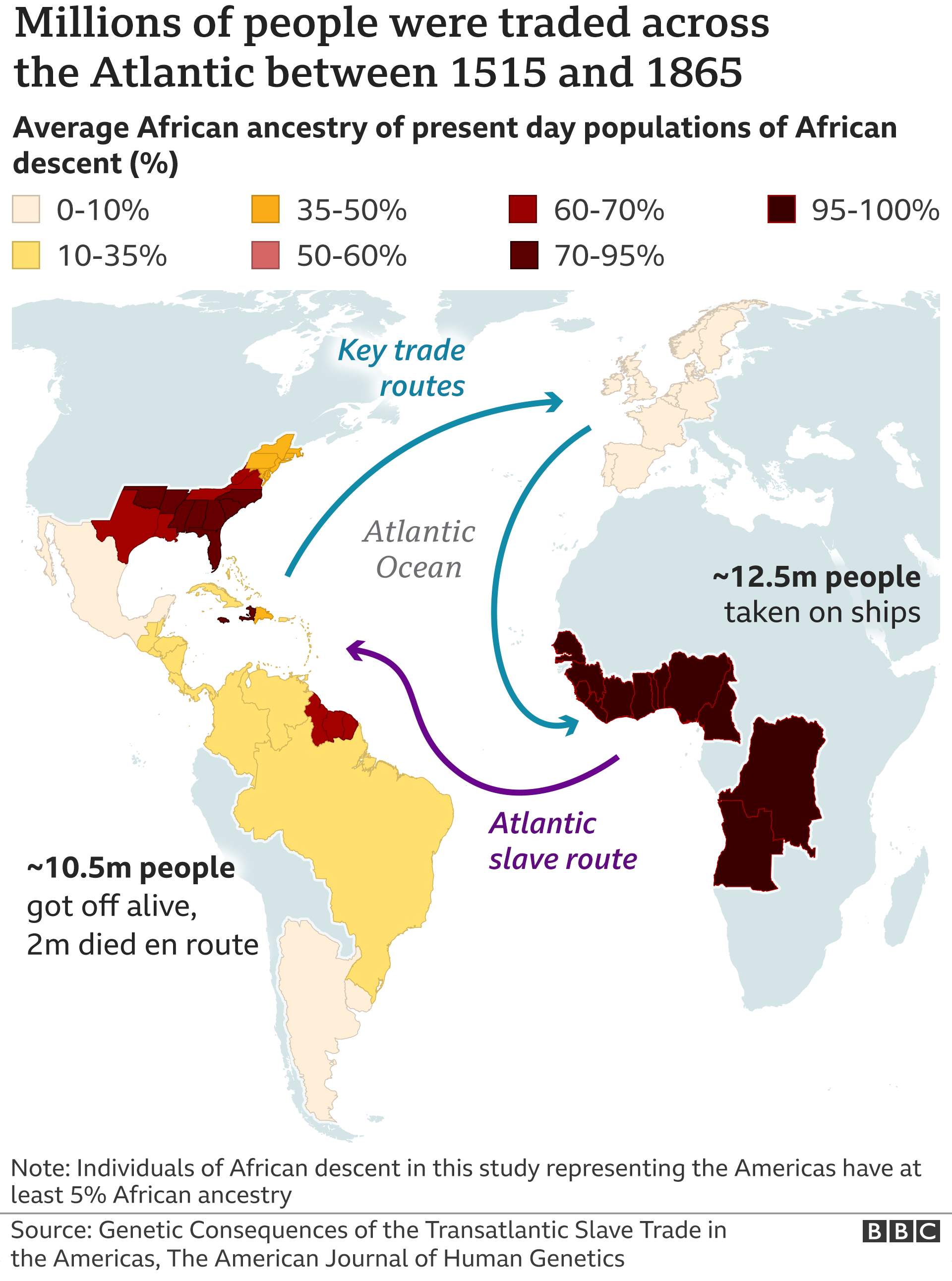
Image: www.bbc.co.uk
Conclusion
Slavery in Africa has had a profound impact on the history and development of the continent. Although the transatlantic slave trade has ended, its legacy continues to shape contemporary issues related to race, identity, and social justice.
It is imperative to acknowledge the suffering and trauma endured by those subjected to slavery and to work towards eradicating all forms of modern slavery.
Are you interested in learning more about the history of slavery in Africa?
Slavery In Africa Before The Slave Trade
FAQ
Q: What were the main causes of slavery in Africa before the transatlantic slave trade?
A: Warfare, raids, economic factors, and social customs contributed to the existence of slavery in various African societies prior to the transatlantic slave trade.
Q: How did the transatlantic slave trade impact slavery in Africa?
A: The transatlantic slave trade introduced a commercialized and dehumanizing form of chattel slavery in Africa. Millions of Africans were forcibly taken from their homelands to be enslaved in the Americas, leading to devastating consequences for individuals, communities, and the continent as a whole.
Q: What were the different forms of slavery that existed in Africa?
A: Slavery in Africa took various forms, including chattel slavery, pledge slavery, domestic slavery, and pawnship or security slavery.
Q: What are the legacies of slavery in Africa today?
A: The legacy of slavery continues to impact race relations, social inequalities, and economic development in Africa. It is important to recognize and address the historical trauma and systemic issues that stem from this period.






