Introduction:
In the ever-fluctuating world of international trade, exchange rate fluctuations present both opportunities and challenges for importers. Understanding how to navigate these fluctuations and mitigate their impact on your business is crucial for long-term success. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of forex gain and loss on imported goods, providing you with the insights and practical strategies to excel in this dynamic environment.

Image: mungfali.com
Understanding Forex Gain and Loss:
When you import goods from a foreign country, you must pay for them in the foreign currency. The exchange rate between your domestic currency and the foreign currency determines the number of domestic currency units you need to acquire the necessary foreign currency. If the exchange rate increases in your favor (appreciation), it means you need fewer domestic currency units to purchase the foreign currency, resulting in a forex gain. Conversely, if the exchange rate moves against you (depreciation), you need more domestic currency units to acquire the foreign currency, resulting in a forex loss.
Impact on Importers:
Forex fluctuations can significantly impact importers’ bottom lines. A sudden depreciation of the domestic currency can lead to substantial forex losses, increasing the cost of imported goods. On the other hand, an appreciation of the domestic currency can result in forex gains, reducing the cost of imported goods. Managing these fluctuations is crucial to ensure stable profitability and minimize financial risks.
Strategies to Mitigate Forex Risk:
To mitigate the impact of forex fluctuations, importers can employ various risk management strategies. Here are some effective approaches:
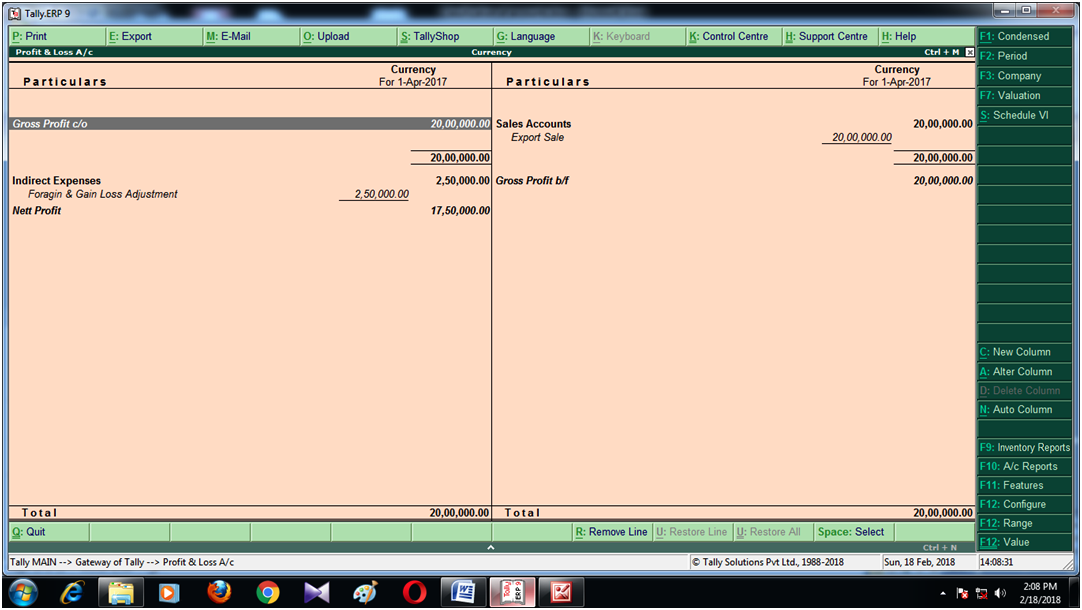
Image: howtotradeonforex.github.io
1. Forward Contracts:
A forward contract is an agreement between two parties to exchange a specific amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. By locking in the exchange rate at the time the contract is entered, an importer can eliminate the risk of adverse fluctuations before making the purchase.
2. Currency Options:
Currency options provide the right, but not the obligation, to exchange a specific amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. Options offer flexibility, allowing importers to exercise their right to convert at a favorable rate only if the exchange rate moves in their favor.
3. Hedging Through Derivatives:
Derivatives, such as futures and options, can be used to create synthetic hedges that protect against currency fluctuations. These instruments allow importers to offset the risk of exchange rate movements without affecting the underlying physical transactions.
4. Natural Hedging:
Natural hedging involves matching your foreign exchange exposures with assets or liabilities in a different currency. For example, an importer can offset forex fluctuations on a euro-denominated import by holding euro-denominated assets.
Staying Informed:
To effectively manage forex gain and loss, staying informed about currency market trends and forecasts is essential. Reading industry publications, subscribing to newsfeeds, and consulting with foreign exchange experts can provide valuable insights into future currency movements. This knowledge enables importers to make informed decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Treatement Forex Gain And Loss On Imported Goods
Conclusion:
Understanding and managing forex gain and loss is a critical aspect of successful importing. By implementing risk management strategies, staying informed about currency market trends, and leveraging expert advice, importers can protect themselves against the impact of exchange rate fluctuations, ensuring long-term profitability and financial resilience. Remember, embracing these strategies is not only an insurance policy against currency volatility but also an opportunity to unlock new opportunities and enhance your business’s competitiveness in the global marketplace.






