Delving into the world of currency trading carries immense potential for financial gain. However, it’s crucial to be cognizant of the tax implications associated with Forex income in New Zealand. Understanding these regulations ensures compliance and maximizes your financial well-being.
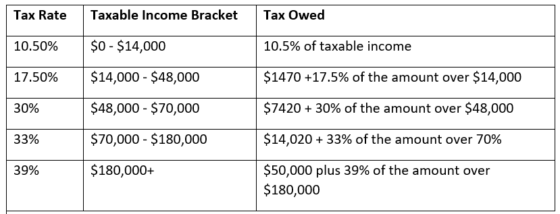
Image: www.canstar.co.nz
Taxation of Forex Income in New Zealand
The New Zealand Inland Revenue Department (IRD) classifies Forex income as business income. Therefore, it is subject to the country’s corporate or individual income tax rates, depending on the trader’s tax status.
For individuals, Forex income is taxed at progressive rates, ranging from 10.5% to 39%. Companies, on the other hand, face a flat corporate tax rate of 28%.
Determining Business Income
Calculating your Forex business income involves subtracting allowable expenses from your gross trading profits. These expenses may include:
- Trading fees and commissions
- Research and subscription costs
- Travel expenses related to trading
- Home office expenses (if applicable)
- Education and training expenses
It’s essential to keep meticulous records of all income and expenses to ensure accurate tax reporting.
Tax Filing Obligations
Individuals and companies involved in Forex trading must file annual tax returns reporting their Forex income. Filing deadlines vary depending on the entity:
- Individuals: 7 July of the following year
- Companies: Within 6 months of the balance date
Additionally, self-employed individuals may be required to make estimated tax payments during the year to avoid potential penalties.

Image: www.treasury.govt.nz
Specific Exemptions
Under certain circumstances, Forex income may be eligible for specific exemptions or concessions:
- Casual Income Exemption: Individuals with annual Forex income below a specified threshold may be exempt from paying taxes on their trading profits.
- FIFO Method: Traders can use the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) method to account for their Forex transactions, which may result in tax savings.
Record Keeping and Compliance
Keeping accurate financial records is crucial for Forex traders. This includes:
- Detailed trading statements
- Proof of expenses incurred
- Copies of Forex transactions
Failing to maintain proper records can lead to tax audits and potential penalties.
Tax On Forex Income In New Zeland
Seek Professional Advice
Taxation of Forex income can be complex. It’s highly recommended to consult with a qualified tax advisor to navigate the regulations and optimize your tax strategy. A professional can provide personalized advice tailored to your specific circumstances, ensuring tax compliance and maximizing your financial success.






