Introduction:
In the intricate world of global finance, the relationship between foreign exchange (forex) markets and interest rates is a dance of interconnected forces, affecting the ebb and flow of economies worldwide. Interest rates, set by central banks, influence the value of currencies, while currency fluctuations impact interest rate policies. Understanding their interplay is crucial for investors, businesses, and governments alike.
Image: nextstepfunded.com
The Interplay of Forex and Interest Rates:
Interest rates, primarily influenced by economic growth, inflation, and monetary policy, act as a magnet for international capital flows. When interest rates are high in one country compared to others, investors tend to invest in that country’s currency, seeking higher returns. This increased demand strengthens the currency, making it more valuable against other currencies.
Conversely, low interest rates can lead to capital outflows, weakening the currency as investors seek better opportunities elsewhere. This interplay is at the heart of forex market dynamics.
Interest Rates and Currency Speculation:
Forex traders closely monitor interest rate movements, using them as signals for currency speculation. When interest rates are expected to rise, traders may buy currencies that are likely to appreciate due to increased demand. Conversely, when interest rates are anticipated to fall, traders may sell those currencies, profiting from their expected devaluation.
Forex Impacts on Interest Rate Policy:
In an interconnected financial world, sharp currency fluctuations can influence interest rate policies. Significant currency depreciation can lead to inflationary pressures, prompting central banks to raise interest rates to stabilize the currency. Conversely, currency appreciation may provide room for lower interest rates, supporting economic growth and stability.
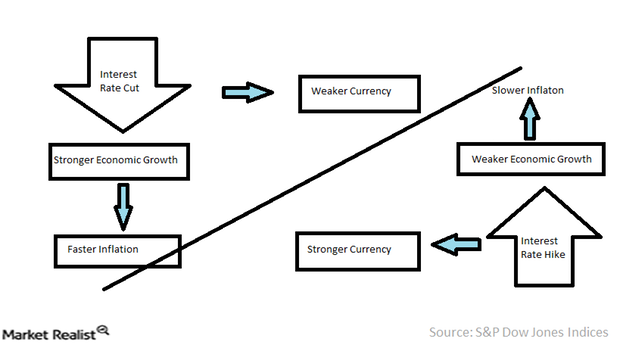
Image: marketrealist.com
Case Studies: The Euro and the US Dollar:
The euro, a major reserve currency, experienced significant fluctuations against the US dollar following the financial crisis of 2008. The European Central Bank (ECB) maintained a low interest rate policy to stimulate economic recovery, weakening the euro compared to the more attractive returns offered by the US dollar.
However, as the US economy recovered and the Federal Reserve raised interest rates, the dollar strengthened, causing the euro to further depreciate. This currency dynamics played a significant role in shaping the investment and economic landscapes of both regions.
The Role of Central Banks:
Central banks play a balancing act, monitoring currency movements and adjusting interest rates accordingly. They aim to maintain stability and prevent extreme fluctuations in exchange rates, which can disrupt trade and economic growth.
Central bank intervention in forex markets, such as buying or selling currencies, can influence currency values and provide stability in times of market volatility. But like a delicate ballet, the art of managing forex and interest rates requires careful judgment and anticipatory action.
Relationship Between Forex And Interest Rates
Cryptocurrency and the Forex-Interest Rate Equation:
The emergence of cryptocurrencies has introduced a new dimension to the forex-interest rate landscape. Cryptos, with their decentralized nature and lack of traditional interest rates, have created a parallel financial system.
The rise of crypto-backed loans and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms is challenging traditional interest rate models and forcing central banks to rethink their approaches to monetary policy.






