Introduction
Image: profitmust.com
In the treacherous waters of financial trading, losses are an inevitable part of the game. However, savvy traders know how to minimize the impact of these setbacks through a crucial risk management tool: the stop loss. A stop loss is an order placed with a broker to automatically sell (or buy in the case of short selling) an asset when it reaches a predetermined price, designed to limit potential losses. Understanding how to calculate stop loss is paramount for any trader seeking to protect their capital while maximizing profit potential.
Types of Stop Loss Orders
Various types of stop loss orders cater to different trading strategies:
- Market Stop Order: An immediate order to sell at the prevailing market price, unconditionally executed regardless of available liquidity.
- Stop-Limit Order: A more cautious approach, placing a sell order only if the market price reaches or exceeds a specified limit price, preventing execution at unfavorable rates.
Calculating Stop Loss Price
The key to effective stop loss placement lies in determining the appropriate stop loss price. There are two main methods:
- Percentage-Based Stop: Calculate a percentage value based on the initial purchase price or the current market price and subtract (or add for short selling) that value to determine the stop loss price.
- Technical Analysis: Utilize technical indicators like moving averages, support and resistance levels, volatility, and risk-reward ratios to objectively determine the optimal stop loss price.
Choosing the Right Stop Loss Price
The ideal stop loss price varies depending on factors such as risk tolerance, trading style, and market conditions.
- Conservative Traders: Opt for tighter stop loss prices closer to the entry price, limiting potential losses but sacrificing profit potential.
- Aggressive Traders: Willing to risk larger losses for the chance of greater gains, they place stop loss orders further away from the entry price.
- Trend Followers: Use trailing stop loss orders that automatically adjust based on market momentum, protecting profits while allowing for favorable trends.
- Volatile Markets: Require wider stop loss prices to avoid premature exits due to sharp price fluctuations.
Optimal Stop Loss Placement Strategies
- Set Stop Loss at Support or Resistance Levels: Identify technical indicators that suggest potential market reversals.
- Use Historical Volatility: Analyze past price movements to determine appropriate stop loss prices based on average fluctuations.
- Calculate Risk-Reward Ratio: Compare potential profit with potential loss to determine an acceptable risk level and corresponding stop loss price.
Conclusion
Calculating stop loss prices is an essential skill for any trader seeking to manage risk effectively. By carefully analyzing market conditions, implementing calculated stop loss strategies, and actively monitoring trades, traders can navigate the ever-changing financial landscape with increased confidence and resilience. Ultimately, understanding how to calculate stop loss unlocks the power to protect profits, preserve capital, and ultimately achieve long-term trading success.
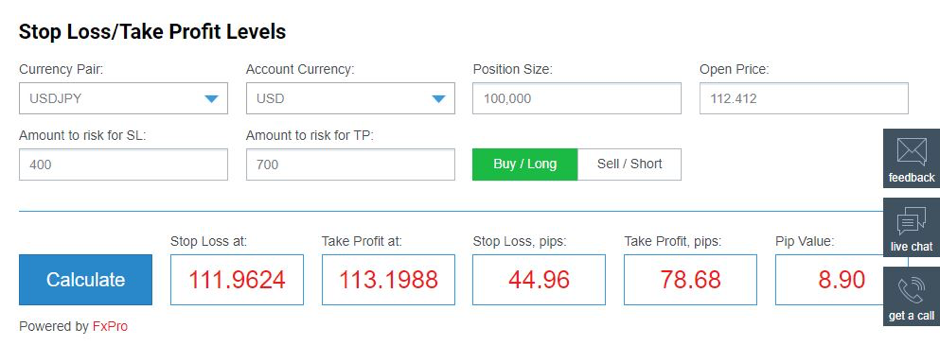
Image: forextraininggroup.com
How To Calculate Stop Loss






