Imagine a world where millions of human beings were forcibly taken from their homes and shipped across the ocean, enduring unspeakable horrors and brutality. This chilling reality was the Transatlantic Slave Trade, a dark chapter in human history that left an irrevocable scar on Africa’s society, economy, and culture. This article delves into the profound effects this tragic event had on the African continent.
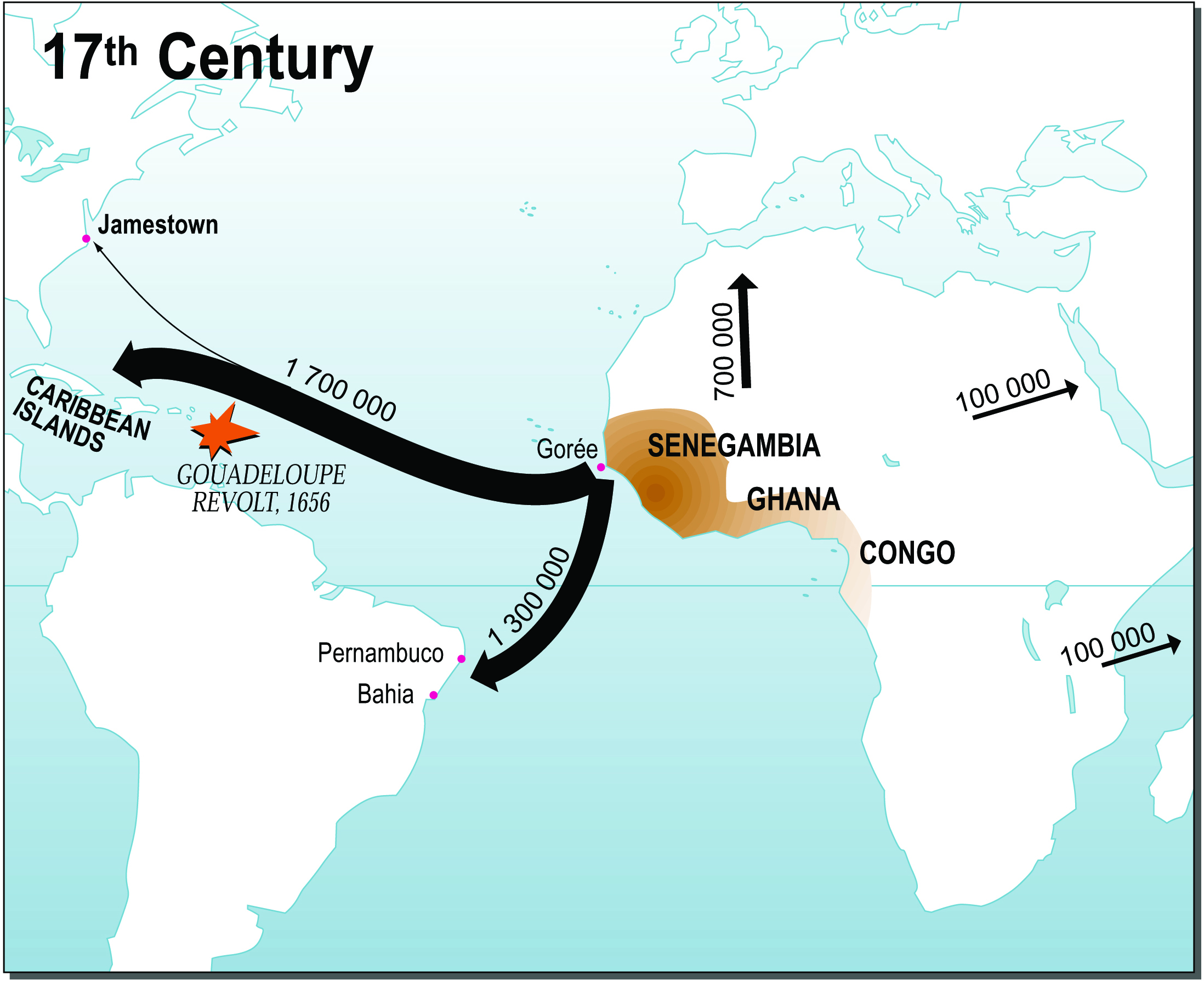
Image: telegra.ph
The Transatlantic Slave Trade, spanning centuries between the 15th and 19th centuries, epitomized the horrors of human avarice and greed. European slave traders, driven by the relentless pursuit of economic gain, descended upon the shores of Africa, capturing millions of individuals from various ethnic and linguistic groups. These individuals, torn from their families and communities, were subjected to unimaginable suffering during the harrowing Middle Passage, a journey that claimed countless lives amidst disease, starvation, and inhuman conditions.
Demographic Catastrophe and Economic Disruption
The mass exodus of millions of Africans had a catastrophic impact on their societies. Communities were decimated, families torn apart, and entire regions depopulated. The loss of such a substantial portion of the population crippled the social and economic fabric of African societies, hindering their development and economic progress. The absence of a skilled labor force disrupted agriculture, trade, and craft industries, leading to a decline in productivity and economic stagnation.
Additionally, the slave trade drained Africa of its most valuable resource: its people. The young, the strong, and the skilled were disproportionately targeted, leaving behind an aging and weakened population. This had long-lasting consequences for Africa’s development, as it deprived the continent of the human capital it needed to build and sustain a thriving economy.
Cultural Erosion and Political Instability
The Transatlantic Slave Trade also profoundly impacted African cultures. The displacement of millions of people resulted in the loss of indigenous languages, traditions, and customs. The cultural diversity that had long characterized Africa was severely diminished as communities were fragmented and cultural continuity disrupted. The slave trade also contributed to political instability, as African societies struggled to cope with the loss of their populations and the traumatic effects of the trade.
Distrust and Division
The legacy of the Transatlantic Slave Trade continues to haunt Africa to this day. It sowed seeds of distrust and division between African nations, as different ethnic and linguistic groups blamed each other for their participation in the slave trade. This distrust hindered cooperation and unity, making it more difficult for African countries to address common challenges and forge a prosperous future.
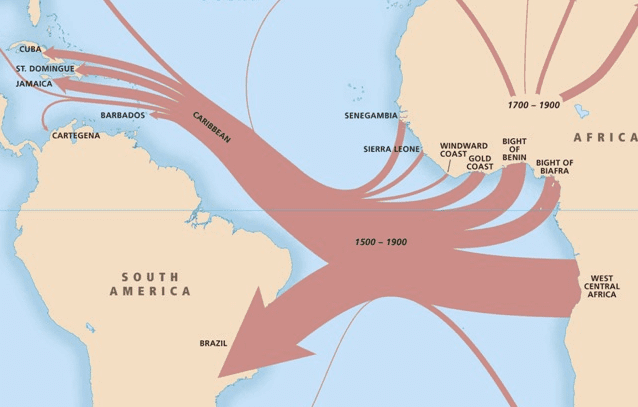
Image: notevenpast.org
Effects Of The Transatlantic Slave Trade On Africa
https://youtube.com/watch?v=uRlMn5jIDEc
A Call for Healing and Reconciliation
The effects of the Transatlantic Slave Trade on Africa were devastating and far-reaching. By acknowledging and understanding this tragic history, we can begin to heal the wounds it inflicted and work towards reconciliation and a better future for Africa. It is essential to promote dialogue, education, and cooperation to overcome the divisions created by the slave trade and build a just and equitable world for all.
In conclusion, the Transatlantic Slave Trade was a monumental tragedy that had a profound impact on Africa’s society, economy, and culture. Its effects continue to resonate today, highlighting the urgent need for reconciliation, dialogue, and healing. By confronting this painful past and working together, we can create a future where the wounds of the past are finally mended, and Africa can reach its full potential.






