Currency trading, also known as foreign exchange (forex) trading, has emerged as a global marketplace where currencies are exchanged 24 hours a day, five days a week. This multi-trillion-dollar industry offers investors and traders an unparalleled opportunity to profit from currency fluctuations. To navigate this complex market successfully, a thorough understanding of its intricate mechanisms is essential. This article delves into the fascinating world of forex trading, exploring its history, fundamental concepts, and practical applications.
Image: www.forex.academy
1. The Historical Genesis of Forex Trading
The concept of exchanging currencies predates recorded history, with early civilizations engaging in barter systems to facilitate trade. However, the modern forex market, as we know it, emerged in the early 20th century with the development of international trade and foreign direct investment. During this time, a network of financial centers, such as London and New York, developed, where banks, corporations, and individuals could exchange currencies to facilitate global transactions. The establishment of the Bretton Woods system in 1944 cemented the U.S. dollar as the world’s reserve currency and instituted fixed exchange rates. However, the collapse of theBretton Woods system in the early 1970s, ushered in a new era of floating exchange rates, which allowed currency values to be determined by supply and demand. The implementation of electronic trading platforms in the 1990s further revolutionized the forex market, paving the way for decentralized and real-time currency trading.
2. Understanding the Basics: The Essence of Forex Trading
At the core of forex trading lies the concept of exchanging one currency for another, based on their respective values. This transaction involves two distinct parties: a seller, who sells a particular currency, and a buyer, who purchases the same currency. Forex traders speculate on the future movement of currency pairs, hoping to profit from fluctuations in their exchange rates. The value of a currency pair is determined by a myriad of factors, including economic data, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
3. Major Currency Pairs and Their Significance
Dominating the forex market are a select group of currencies known as major currency pairs. These pairs account for the bulk of trading volume and typically involve the U.S. dollar (USD) on one side. The most frequently traded currency pairs include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, and USD/CAD. These pairs are highly liquid, meaning they can be traded in large volumes with minimal impact on their price. They also represent the economic strength and stability of the underlying countries.
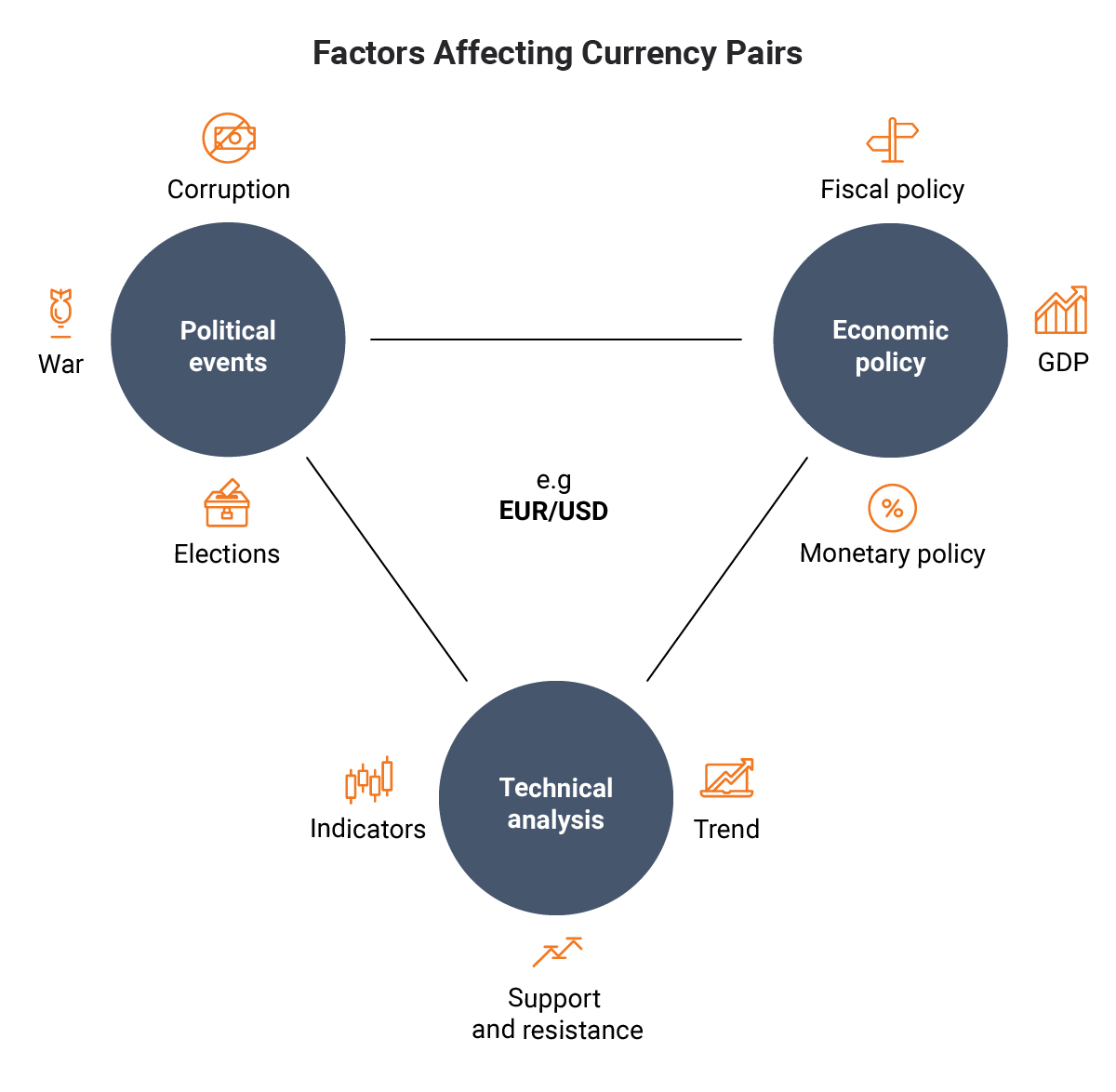
Image: www.ainfosolutions.com
4. Navigating the Forex Market: Spot, Forward, and Futures Contracts
Forex trading can be conducted in various forms, the most common being spot, forward, and futures contracts. A spot contract is an immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. In a forward contract, buyers and sellers agree to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a specific future date. Futures contracts, on the other hand, are standardized contracts traded on exchanges, requiring buyers and sellers to fulfill their obligations to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a set price on a predetermined date.
5. The Interplay of Leverage and Risk Management in Forex Trading
Leverage is a double-edged sword that amplifies both potential profits and losses in forex trading. Forex brokers offer leverage ranging from 10:1 up to 500:1, which allows traders to enter positions significantly larger than their account balance. While leverage can magnify gains, it can also lead to substantial losses, especially in volatile market conditions. Effective risk management strategies, such as establishing stop-loss orders and carefully managing position sizes, are crucial for mitigating the perils associated with leverage.
6. Technical Analysis: Unveiling Market Trends and Patterns
Technical analysis is a popular method of forecasting future currency movements by analyzing historical price data. This approach assumes that past price patterns and trends can provide valuable insights into market behavior. Technical analysts employ various charts and indicators, such as candlestick charts, moving averages, and Bollinger Bands, to identify potential trading opportunities. While technical analysis can be a useful tool, it’s important to remember that it’s not an exact science, and its accuracy can vary significantly depending on market conditions.
7. Fundamental Analysis: Deciphering Economic Indicators
Fundamental analysis delves into the underlying economic factors that drive currency markets. This approach involves analyzing macroeconomic data, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, trade balances, and interest rates. Fundamental analysis seeks to determine the intrinsic value of a currency by evaluating the economic health and stability of the country that issues it. Understanding these factors helps traders gauge the potential direction of currency movements and make informed trading decisions.
8. Currency Trading Platforms: Gateways to the Forex Market
Navigating the forex market requires a reliable and efficient currency trading platform. These platforms provide traders with access to real-time market data, charting tools, and order execution capabilities. Choosing the right platform depends on a trader’s individual needs and preferences. Factors to consider include the platform’s user interface, ease of use, functionality, and the availability of features such as technical analysis tools and mobile trading.
9. Forex Trading Strategies: A Multitude of Approaches for Market Mastery
The realm of forex trading encompasses a diverse range of strategies employed by traders to maximize their profits. These strategies can be broadly categorized into three main types: scalping, day trading, and swing trading. Each strategy offers its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks and caters to the individual risk tolerance and time commitments of the trader. Scalping involves taking numerous small profits from short-term price movements, while day trading seeks to profit from intraday price fluctuations. Swing trading involves holding positions for a few days to several weeks, capitalizing on larger market trends.
Mechanism Of Currency Trading In Forex
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of forex trading is a journey that requires both knowledge and experience. This article has provided a comprehensive guide to the mechanisms of currency trading, from its historical roots to the practical applications used by modern traders. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or embarking on your trading adventure, a thorough grasp of this dynamic market is essential for navigating its complexities and maximizing your potential profits.






