Introduction
In the fast-paced and ever-changing world of forex trading, traders constantly seek tools to stay ahead of market movements and maximize profits. Among the diverse array of analytical tools available, momentum indicators stand out for their ability to identify and capitalize on the underlying trend. By measuring the rate of change in price, these indicators provide valuable insights into the strength and direction of market momentum, allowing traders to make informed trading decisions.
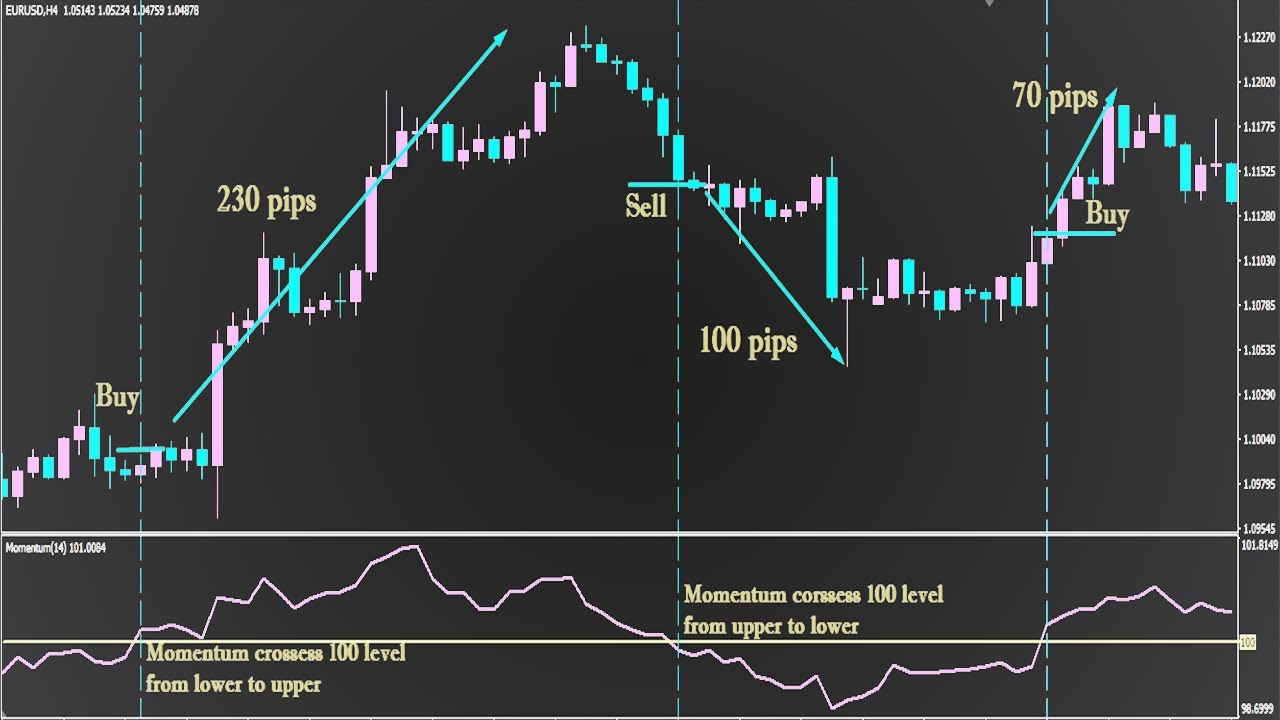
Image: tradingforexguide.com
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of momentum indicators, exploring their history, fundamental principles, and practical applications in forex trading. We will also shed light on the latest advancements in this domain, empowering traders with the knowledge they need to harness the power of momentum in their trading strategies.
Understanding Momentum and Its Significance
Momentum, in the context of forex trading, refers to the extent and speed at which the price of a currency pair moves. It reflects the strength of the underlying buying or selling pressure, providing valuable cues about the future direction of price action. Momentum indicators are designed to measure this momentum, helping traders gauge the speed and persistence of price swings.
Indicators quantify momentum by analyzing price data over a specific period of time. They assign numerical values to the rate of price change, allowing traders to visualize and interpret the strength and direction of momentum. Volatility and market trends can be effectively assessed using these indicators, offering crucial insights into potential trading opportunities.
Types of Momentum Indicators in Forex Trading
The forex market offers a wide range of momentum indicators, each with its unique characteristics and methodology. Some of the most commonly used include:
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes, indicating whether the currency pair is overbought or overbought. Overbought conditions, where RSI values exceed 70, suggest potential price reversals, while oversold values below 30 can indicate buying opportunities.

Image: www.fcxchief.com
2. Stochastic Oscillator (%K and %D)
The Stochastic Oscillator compares the price of a currency pair to its price range over a specified period. The %K line represents the current RSI value, while the %D line is a moving average of %K. Traders can identify bullish or bearish trends and potential trading opportunities based on the position of these lines relative to overbought or oversold levels.
3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
MACD measures the difference between two exponential moving averages (EMAs), reflecting the divergence between short-term and long-term momentum. Its accompanying lines, the signal line and the histogram, provide further insights into market momentum and potential trading signals.
4. Rate of Change (ROC)
ROC measures the percentage change in price over a specific period of time. Positive ROC values indicate upward momentum, while negative values suggest downward momentum. Extreme ROC readings can signal potential overbought or oversold conditions.
Interpreting Momentum Indicator Signals
Traders must interpret momentum indicator signals in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis to make informed trading decisions. This includes evaluating indicators’ values, slopes, and positions relative to overbought and oversold levels.
-
Bullish Signal: Momentum indicators trending above their neutral lines, forming higher highs, or crossing bullish threshold levels (e.g., 50 for RSI) indicate positive momentum and potential buying opportunities.
-
Bearish Signal: Indicators trending below their neutral lines, forming lower lows, or crossing bearish thresholds (e.g., 30 for RSI) suggest negative momentum and potential selling opportunities.
-
Divergence Signal: Divergence occurs when the momentum indicator signals a trend opposite to the price action. This can indicate a potential reversal or a continuation of the current trend.
Limitations of Momentum Indicators
While momentum indicators are valuable tools, it is important to understand their limitations:
-
Lagging Indicators: Momentum indicators are based on past price data and can often lag behind price action. Traders must be cautious about relying solely on these indicators for real-time trading decisions.
-
False Signals: Momentum indicators can generate false signals, particularly during periods of market volatility or consolidation. Traders should be aware of these potential limitations and confirm signals using other forms of analysis.
-
Overreliance on Parameters: Momentum indicators’ performance is highly dependent on the chosen parameters, such as the period and type of moving averages used. Traders must experiment with different parameter settings to find what works best for their trading strategy.
Indicator Know The Momentum In Forex Strategy
Conclusion
Momentum indicators play an integral role in forex trading, offering insights into the rate of price change and the underlying market sentiment. By understanding the principles and mechanics of momentum indicators, traders can develop effective trading strategies that capitalize on momentum trends. However, it is crucial to be mindful of the limitations of these indicators and to use caution when interpreting their signals. Traders must constantly monitor market conditions, incorporate different forms of analysis, and exercise disciplined risk management practices to maximize their success in the ever-evolving forex market.






