Introduction:
India’s foreign exchange reserves, once a bastion of strength for the economy, have been on a steady decline since reaching their peak in 2021. This decline has far-reaching implications for the Indian economy, particularly for the value of the Indian rupee. In this article, we delve into the factors behind this decline, analyze its impact on the rupee, and explore the potential consequences for the country’s economic trajectory.

Image: www.inventiva.co.in
Factors Contributing to the Decline:
The depletion of India’s forex reserves can be attributed to several key factors:
- Falling Exports: Weakening global demand and the Russia-Ukraine conflict have led to a decline in Indian exports, thereby reducing the inflow of foreign currency.
- Rising Imports: India’s dependence on imports for essential commodities like oil and coal has increased, resulting in a significant outflow of foreign exchange.
- Capital Outflows: Foreign investors have withdrawn funds from the Indian stock market due to global economic uncertainty, contributing to the forex reserve decline.
- Currency Intervention: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been intervening in the foreign exchange market to support the value of the rupee, which has further depleted reserves.
Impact on the Rupee:
The decline in forex reserves has had a significant impact on the value of the Indian rupee. As of May 2023, the rupee has depreciated by over 5% against the US dollar compared to the same period last year. The depreciation has been driven by the following factors:
- Reduced Demand for Rupee: With the fall in forex reserves, the ability of the RBI to defend the rupee’s value has diminished. This has resulted in reduced demand for the rupee from foreign investors and businesses.
- Increased Supply of Rupee: The decline in exports and capital inflows has led to a higher supply of the rupee in the foreign exchange market, further contributing to its depreciation.
- Global Economic Factors: The strengthening of the US dollar and the tightening monetary policy by the Federal Reserve have also played a role in the depreciation of the rupee.
Consequences for the Economy:
The depreciating rupee has both positive and negative consequences for the Indian economy:
Positive Consequences:
- Boosts Exports: A weaker rupee makes Indian exports more competitive in the global market, potentially leading to increased revenue for exporters.
- Reduces Imports: The depreciation of the rupee acts as a deterrent to imports, as they become more expensive. This can help reduce the country’s import bill.
Negative Consequences:
- Higher Inflation: A depreciating rupee leads to imported goods becoming more expensive, pushing up inflation.
- Higher External Debt Burden: India has substantial external debt denominated in foreign currencies. A weaker rupee increases the cost of servicing this debt.
- Reduced Investment: The depreciation of the rupee makes it more challenging for foreign investors to invest in India, potentially hampering economic growth.
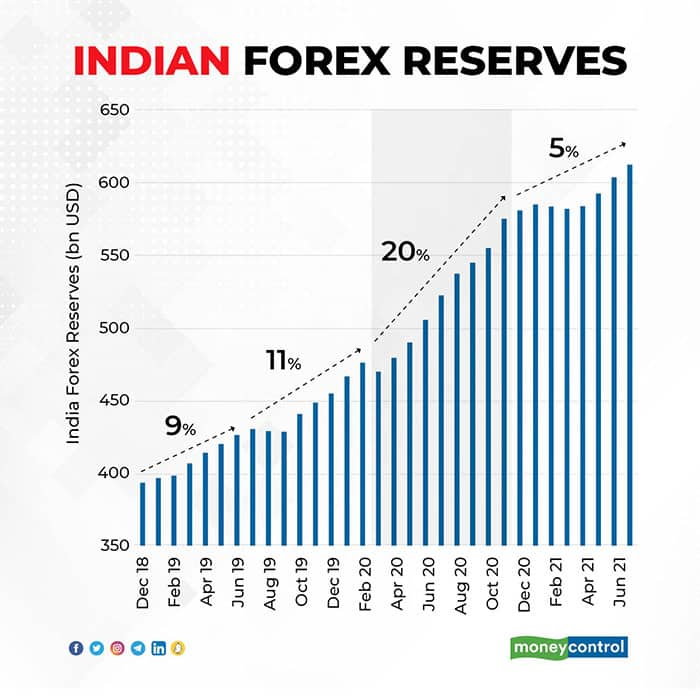
Image: www.moneycontrol.com
Policy Response and Outlook:
The RBI has taken steps to stem the decline of forex reserves and support the rupee’s value, including:
- Interest Rate Hikes: The RBI has increased interest rates in an effort to curb capital outflows and attract foreign capital.
- Forex Market Intervention: The RBI has been intervening in the foreign exchange market by selling US dollars to support the rupee.
- Capital Controls: The government has implemented some capital controls to restrict the outflow of foreign funds.
The outlook for India’s forex reserves and the rupee remains uncertain, as it is heavily influenced by global economic conditions and geopolitical factors. However, if the factors contributing to the decline persist, the RBI may have to implement more aggressive measures to stabilize the forex reserves and support the rupee’s value.
India’S Forex Reserve If Declaned Then Rupee
Conclusion:
India’s declining forex reserves and the subsequent depreciation of the rupee have significant implications for the country’s economy. While some positive outcomes may arise, such as boosted exports, there are also potential risks like higher inflation and a reduced investment climate. The RBI’s policy response and the future direction of the global economy will play a critical role in shaping the trajectory of India’s forex reserves and the value of the rupee.






