Introduction
In the intricate realm of international trade and finance, foreign exchange (forex) risk poses a constant challenge, threatening to erode profits and destabilize financial positions. Forex risk, simply put, is the potential loss or gain that can occur when a trader or investor converts one currency into another. Understanding and implementing effective strategies to reduce forex risk is crucial for individuals and businesses that engage in cross-border transactions. This comprehensive guide will delve into proven techniques and best practices to mitigate forex risk, ensuring that traders and investors navigate the complexities of global finance with confidence.
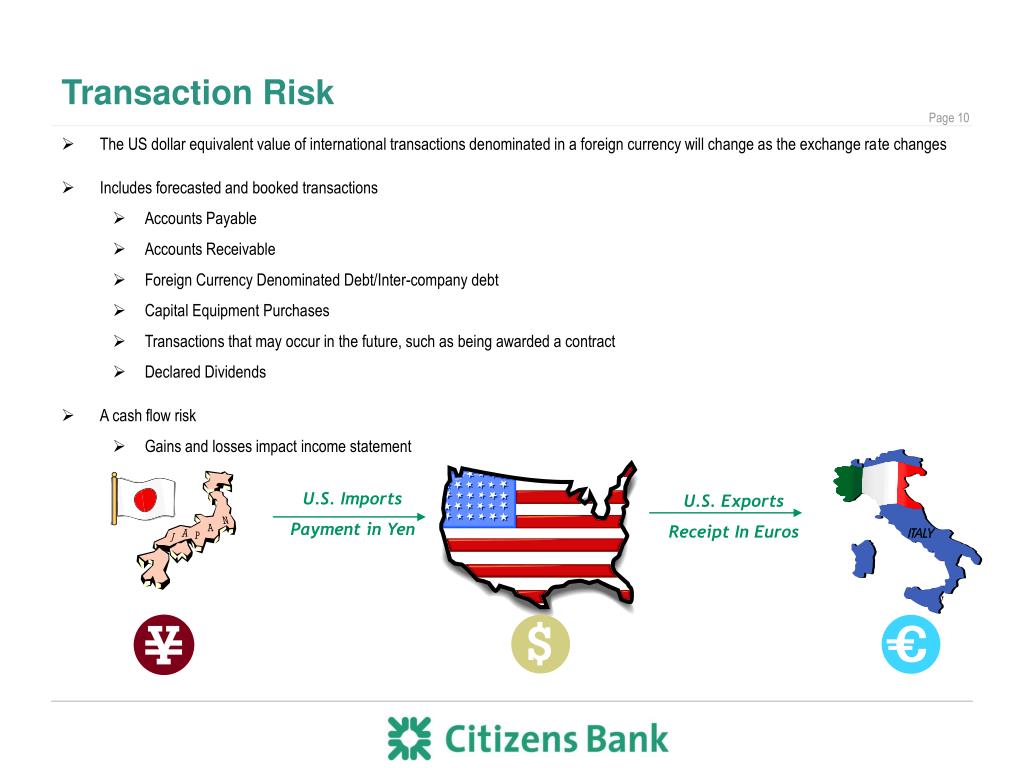
Image: www.slideserve.com
Understanding Forex Risk
Forex risk stems from the constant fluctuations in exchange rates between different currencies. These fluctuations can be influenced by various macroeconomic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, political stability, and economic data. For example, if a U.S. exporter sells goods to a customer in the Eurozone and receives payment in euros, the exporter’s U.S. dollar revenue will be subject to fluctuations in the euro-dollar exchange rate.
Common Types of Forex Risk
- Transaction Risk: The risk of exchange rate changes between the time a transaction is initiated and when it is settled.
- Translation Risk: The risk of exchange rate changes affecting the financial statements of multinational companies with operations in multiple countries.
- Economic Risk: The risk that changes in exchange rates will impact a country’s economic growth, inflation, and overall financial stability.
Strategies to Reduce Forex Risk
Image: howtotrade.com
1. Hedging with Forward Contracts
Forward contracts provide a means of locking in an exchange rate for a future date, reducing the risk of adverse fluctuations. By entering into a forward contract, the trader or investor agrees to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a specific future date, effectively eliminating the uncertainty associated with future exchange rate movements.
2. Currency Options
Currency options offer another hedging instrument, granting the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell a currency at a specified price (the strike price) before a certain date (the expiration date). With a call option, the trader has the right to buy the currency, while with a put option, they have the right to sell. Options provide flexibility and tailored risk management, allowing traders to protect against favorable or unfavorable exchange rate movements.
3. Natural Hedging
Natural hedging involves matching assets and liabilities in different currencies to offset potential gains and losses from exchange rate fluctuations. For example, a company with subsidiaries in multiple countries can use its earnings in one currency to meet its obligations in another, reducing the overall exposure to forex risk.
4. Diversification
Diversification across different currencies and geographic regions can help spread forex risk. By investing in assets denominated in multiple currencies, traders and investors can potentially reduce the impact of currency fluctuations on their overall portfolio.
5. Monitoring and Forecasting
Regularly monitoring exchange rate trends and economic indicators can provide valuable insights into potential risks. Staying informed about economic events, such as central bank policy changes or political developments, allows traders and investors to adjust their risk management strategies accordingly.
How To Reduce Forex Risk
Conclusion
Forex risk is an inherent part of international finance, but it can be effectively managed and mitigated through the implementation of sound strategies. By understanding the types of forex risk, employing hedging instruments such as forward contracts and currency options, pursuing natural hedging opportunities, diversifying across currencies and regions, and diligently monitoring market conditions, traders and investors can navigate the complexities of forex risk with increased confidence and resilience. Remember, reducing forex risk is not about eliminating it entirely but rather minimizing its potential impact on financial stability and overall investment outcomes.






