In the ever-evolving financial landscape, foreign exchange (forex) trading has emerged as a prominent activity, connecting global markets and facilitating international commerce. With the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, forex transactions have come under scrutiny, warranting a thorough understanding of their tax implications. This comprehensive article endeavors to shed light on the GST framework applicable to forex sales, guiding traders in navigating this complex landscape.

Image: www.betterplace.co.in
Forex trading, defined as the buying and selling of currencies, has become a popular investment avenue for individuals and businesses alike. The GST, a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services, has brought forex transactions within its ambit. The GST Council, the apex decision-making body for indirect taxation in India, has categorized forex trading as a financial service under the GST regime, subject to specific tax regulations.
GST Rate on Forex Sale
As per the GST regulations, the sale of foreign currency attracts a GST rate of 18%. This tax rate applies to the difference between the selling price and the cost of acquisition of the foreign currency, also known as the ‘spread’ or ‘mark-up.’ It’s important to note that the GST liability arises only on the profit earned by the forex trader, not on the entire transaction amount.
For instance, if a forex trader purchases 100 US dollars at a rate of Rs. 80 per dollar and subsequently sells it at Rs. 82 per dollar, the GST liability would be calculated as follows:
Selling Price: Rs. 8200
Cost of Acquisition: Rs. 8000
Spread (Profit): Rs. 200
GST (18% on Spread): Rs. 36
Therefore, the trader would be required to pay Rs. 36 as GST on this transaction.
Input Tax Credit and Reverse Charge Mechanism
Like other business entities, forex traders are eligible for Input Tax Credit (ITC) on GST paid on their purchases. ITC refers to the deduction of GST paid on inputs from GST payable on outputs. This mechanism prevents double taxation and ensures smooth flow of tax credits across the supply chain.
In cases where the supplier of forex services is located outside India, the reverse charge mechanism is applicable. Under this mechanism, the recipient of services (i.e., the forex trader) becomes liable to pay GST on behalf of the supplier. The GST liability is calculated in the same manner as if the supplier were located in India, and the trader is required to file GST returns and pay the tax accordingly.
GST Compliance for Forex Traders
Forex traders must comply with various GST requirements to ensure adherence to tax regulations. These include:
- Registration under GST if their annual turnover exceeds the threshold limit.
- Filing regular GST returns, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis.
- Maintaining proper records of all forex transactions, including invoices, contracts, and account statements.
- Paying GST dues on time through the GST portal.
Failure to comply with GST regulations can attract penalties and other legal consequences. Forex traders are advised to consult with tax experts to ensure they stay up-to-date with the latest GST requirements and fulfill their compliance obligations promptly.
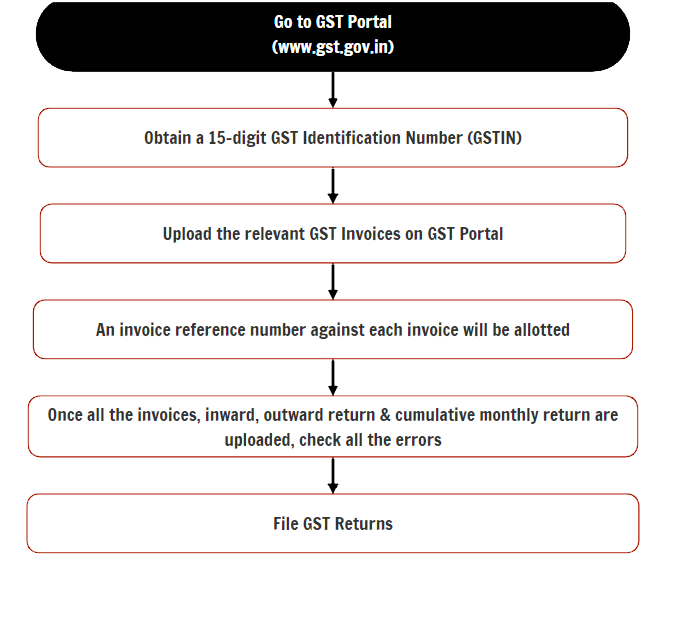
Image: www.taxhelpdesk.in
Impact of GST on Forex Trading
The introduction of GST has had a significant impact on forex trading in India. While the GST framework provides clarity and uniformity in taxation, it has also brought additional compliance burden for traders.
On the positive side, GST has simplified the tax structure for forex traders by eliminating multiple indirect taxes such as service tax, excise duty, and VAT. The GST portal has also streamlined the process of filing GST returns and paying taxes.
On the flip side, the GST liability on forex transactions has increased the overall cost of trading for some traders. Moreover, the reverse charge mechanism can be complex to implement, especially for small businesses.
Gst On Sale Of Forex
Conclusion
The GST framework for forex trading provides a clear and comprehensive framework for taxation of this important financial activity. By understanding the GST rate applicable to forex sales, input tax credit and reverse charge mechanisms, and compliance requirements, forex traders can ensure they fulfill their GST obligations and navigate this complex landscape effectively.
As the GST regime continues to evolve, it is crucial for forex traders to stay abreast of the latest regulatory changes and seek guidance from tax professionals when needed. By embracing transparency and compliance, forex traders can contribute to the overall efficiency and integrity of the financial system in India.






