Imagine you’re a trader navigating the turbulent waters of the foreign exchange market, where every decision holds the potential for both triumph and adversity. Amidst this volatile landscape, you stumble upon a crucial concept: gap limits. They’re the invisible barriers that govern how much price can fluctuate within a given time frame.
Image: www.forex.academy
In the world of Forex, understanding gap limits is not merely an academic exercise; it’s a matter of self-preservation. Just as a ship’s hull protects its crew from the unforgiving ocean, knowledge of gap limits shields traders from the potentially catastrophic consequences of unpredictable price movements.
What Are Gap Limits in Forex?
Gap limits are a fundamental aspect of Forex trading, akin to the rules of a game. They establish the maximum difference in price that can occur between two consecutive traded prices. The rationale behind these limits is to prevent excessive volatility and maintain market stability.
Simply put, gap limits ensure that prices don’t jump or drop too drastically in a short period. It’s like having a traffic light on a busy highway, preventing cars from crashing into each other.
The Significance of Gap Limits for Forex Traders
For Forex traders, grasping the implications of gap limits is paramount. These caps can have a profound impact on trading strategies and risk management.
Think of it this way: if gap limits were non-existent, the Forex market would be a wild west, where prices could fluctuate erratically, leaving traders vulnerable to devastating losses. Gap limits act as a safety net, mitigating extreme price swings and providing traders with a more predictable trading environment.
How Do Gap Limits Work?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the central bank of India, sets gap limits for various currency pairs traded on the Indian Forex market. These limits vary depending on the currency pair and the time of day.
During market hours, gap limits are typically narrower, allowing for a more controlled price movement. However, in times of high volatility, such as during news announcements or economic events, the RBI may widen the gap limits to facilitate necessary price adjustments.
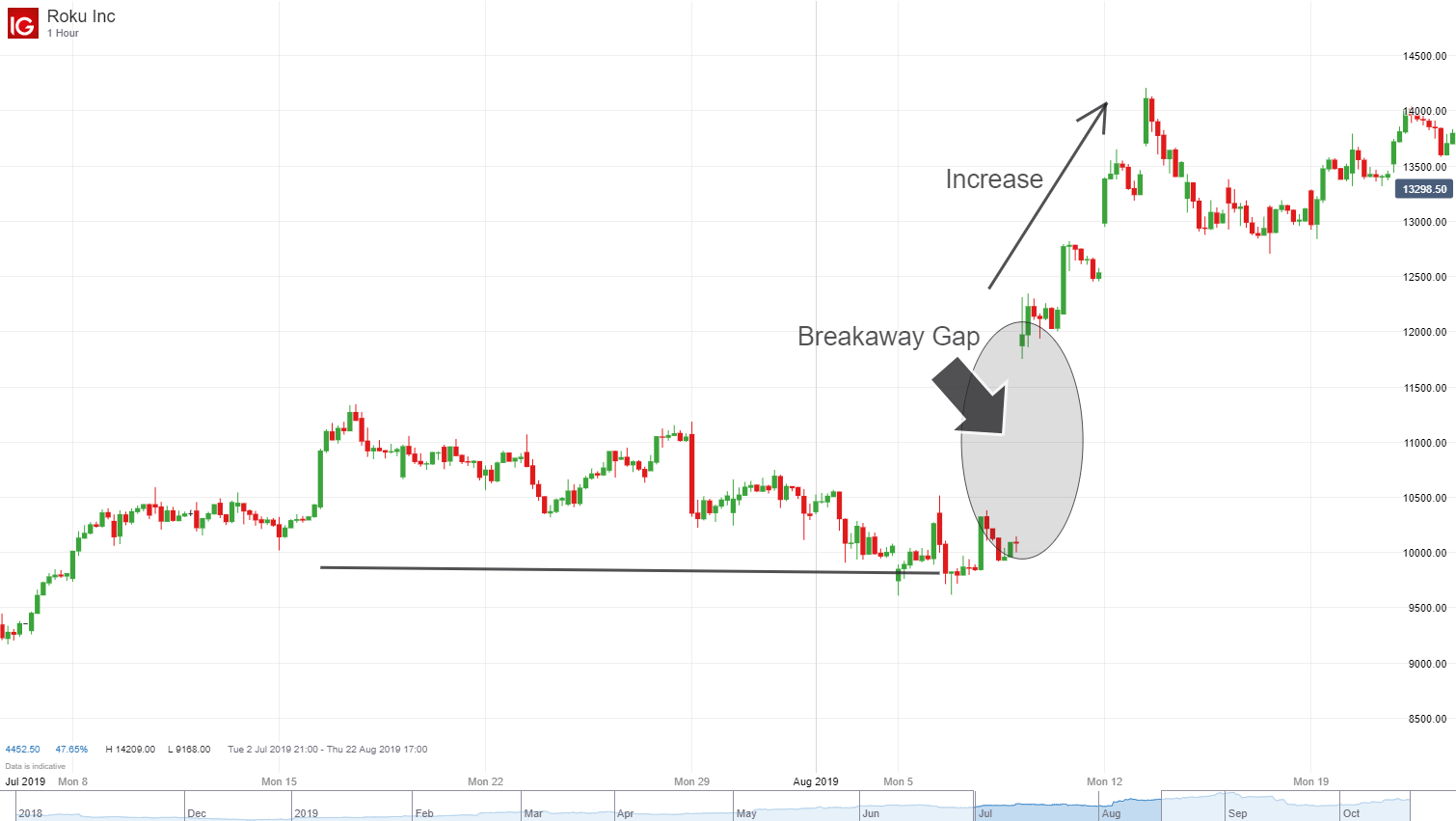
Image: www.dailyfx.com
Gap Limits vs. Stop-Loss Orders
Gap limits and stop-loss orders are two distinct risk management techniques, each playing a crucial role in Forex trading.
Stop-loss orders are placed at a predetermined price level, triggering an automatic closure of the trade if the market price reaches that level. They help traders limit their potential losses in the event of adverse price movements.
Gap limits, on the other hand, are imposed by the market itself and cannot be modified by individual traders. They act as an additional layer of protection, preventing extreme price fluctuations that could override stop-loss orders and lead to substantial losses.
Trading Strategies Considering Gap Limits
Savvy traders consider gap limits when formulating their Forex trading strategies. One common approach is to widen stop-loss levels during periods of expected volatility to accommodate for potential price gaps.
Another strategy involves incorporating gap limits into technical analysis, identifying potential support and resistance levels based on historical price movements within these limits. By understanding the constraints imposed by gap limits, traders can navigate the Forex market more effectively and manage their trading risks prudently.
Gap Limits In Forex By Rbi
Conclusion
Gap limits in Forex are an indispensable component of market stability and risk management for traders. By understanding these invisible boundaries, traders can minimize the potential consequences of unpredictable price movements and make informed trading decisions.
Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting your journey in the foreign exchange market, acknowledging gap limits is crucial. Embrace them as your allies, guiding you through the ever-changing landscape of Forex trading and empowering you to navigate its challenges with greater confidence and success.






