Introduction
In today’s interconnected global economy, foreign exchange (forex) trading plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and investments. For aspiring professionals pursuing an MCom degree specializing in finance and accounting, a thorough understanding of forex is paramount. This article delves into the intricacies of forex trading, providing an in-depth exploration of key concepts, applications, and market dynamics.
Defining Forex: The Basics
Forex refers to the decentralized global financial market where currencies are bought, sold, and exchanged across national borders. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an estimated daily trading volume of trillions of US dollars. Unlike traditional stock markets that operate on a centralized exchange, forex transactions occur over-the-counter (OTC) among various participants, including banks, financial institutions, hedge funds, and individual traders.
Components of the Forex Market
The forex market is comprised of three main components:
- Spot Market: Facilitates immediate purchase and sale of currencies at the current exchange rate.
- Forward Market: Allows traders to buy or sell currencies at a specific exchange rate for a future delivery date, typically ranging from days to months or even years.
- Options Market: Provides the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell a specific currency at a designated price on or before a specified date.
Major Currency Pairs
Forex trading primarily involves trading currency pairs, which represent the exchange rate of one currency against another. The most commonly traded currency pairs are known as “majors,” including EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, and USD/CAD. These pairs account for a significant portion of global forex transactions.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Exchange rates in the forex market are constantly fluctuating, influenced by a multitude of interconnected factors, such as:
- Economic Conditions: Growth, inflation, unemployment, and interest rates.
- Political Events: Elections, policy changes, and geopolitical tensions.
- Monetary Policy: Interest rate adjustments, foreign exchange interventions, and quantitative easing.
- Supply and Demand: Market sentiment, speculation, and trade patterns.
Types of Forex Traders
There are different types of traders in the forex market, each with varying strategies and risk appetites:
- Scalpers: Aim for quick profits by trading on short-term price fluctuations.
- Day Traders: Open and close positions within the same trading day.
- Swing Traders: Hold positions for a few days or weeks, targeting larger price movements.
- Trend Traders: Analyze long-term market trends and trade accordingly.
- Carry Traders: Exploit interest rate differentials between currencies.
Benefits of Forex Trading
Forex trading offers several advantages for participants:
- 24/7 Market Access: Global reach and flexibility with trading around the clock.
- High Liquidity: The largest and most liquid financial market, ensuring quick execution of trades.
- Leverage: Ability to increase trading capital using leverage, potentially enhancing profits.
- Speculation Opportunities: Profit from both rising and falling currency prices.
Risks of Forex Trading
Forex trading also carries inherent risks that should be considered:
- Volatility: Fluctuating exchange rates can result in significant losses.
- Leverage: While leverage can magnify profits, it can also amplify losses.
- Counterparty Risk: Transactions are only as secure as the financial institutions involved.
- Technical Knowledge: Successful trading requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and risk management.
Conclusion
Forex trading is an intricate and multifaceted financial arena that offers both opportunities and risks. By comprehending the fundamental concepts, trading mechanisms, and external factors influencing exchange rates, MCom students can gain valuable knowledge and insights into this dynamic market. However, it is crucial to approach forex trading with a balanced perspective, acknowledging the inherent risks and preparing appropriately. For aspiring finance professionals seeking to navigate the ever-evolving global economy, a thorough understanding of forex remains an essential asset.
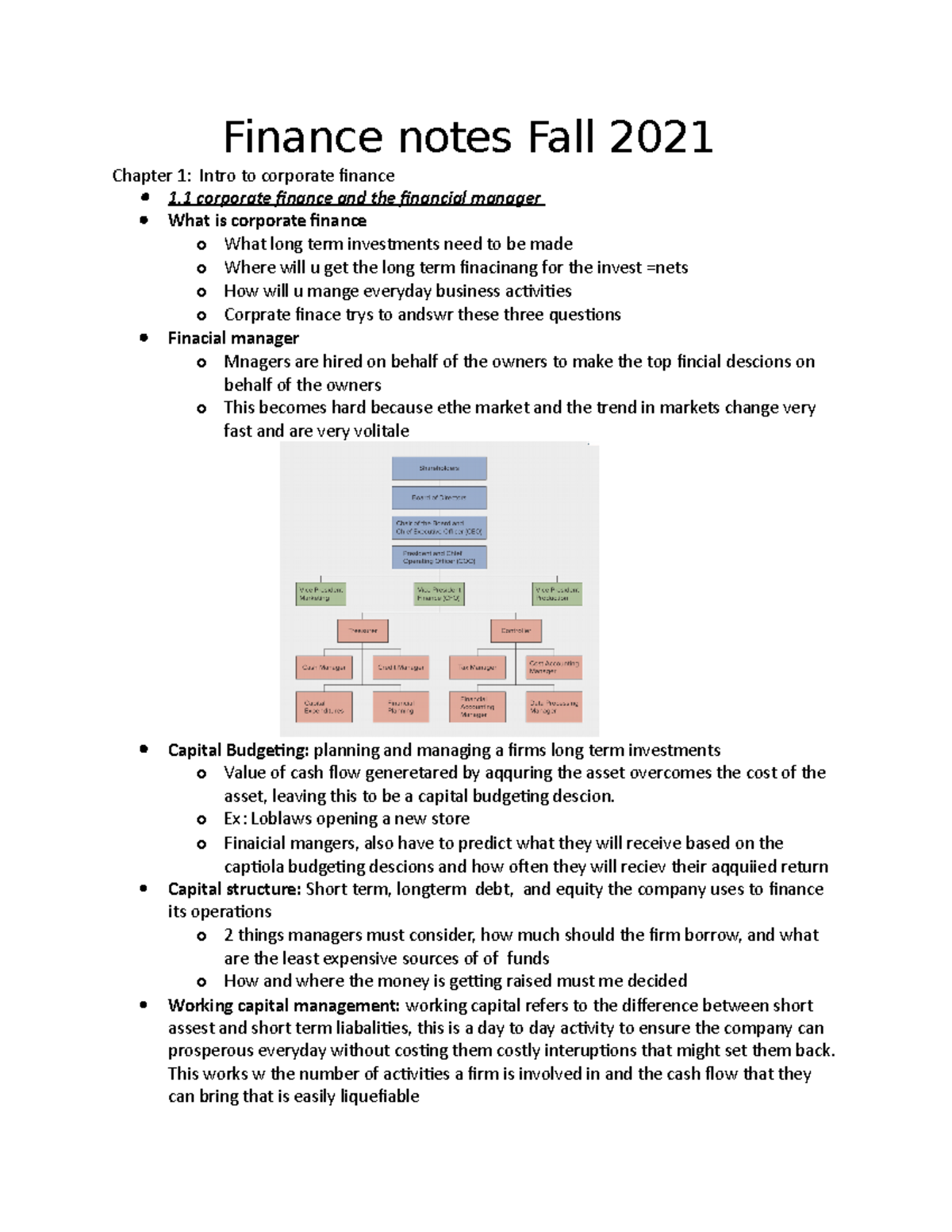
Image: www.studocu.com

Image: www.studocu.com
Forex Chap 2 Mcom 2nd Semester Mcom






