India’s foreign exchange reserves, a vital component of its economic stability, play a crucial role in safeguarding the nation against external financial shocks and ensuring sustainable growth. Composed of diverse assets held by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), these reserves serve as a cushion against global economic uncertainties, facilitating international payments and boosting investor confidence.

Image: twitter.com
Understanding the Components of India’s Forex Reserves:
India’s forex reserves comprise a range of assets, each serving a specific purpose within the broader reserve management strategy. These components include:
Gold: A Traditional Bulwark of Stability
Gold, a precious metal renowned for its intrinsic value, constitutes a substantial portion of India’s reserves. Its inclusion as a safe haven asset ensures a hedge against market volatility and economic uncertainties.
Foreign Currency Assets: Navigating the Global Exchange
Foreign currency assets, primarily consisting of investments in government bonds, treasury bills, and other sovereign debt instruments of developed countries, account for a significant share of India’s reserves. These investments provide a stable income stream while simultaneously diversifying the reserve portfolio.
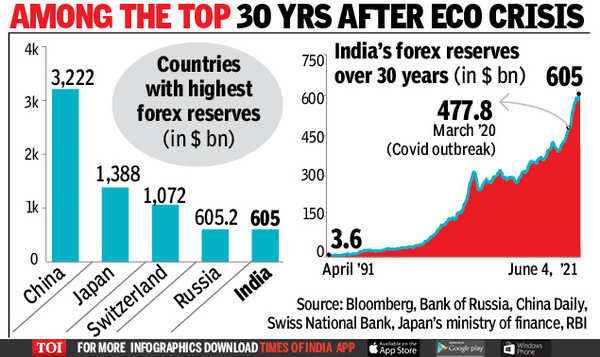
Image: currentaffairs.adda247.com
Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): Beyond Traditional Currencies
Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), issued by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), are a supranational reserve asset that supplement traditional foreign exchange reserves. Their inclusion in India’s portfolio provides additional liquidity and resilience.
Reserve Tranche Position: India’s Standing at the IMF
India’s reserve tranche position with the IMF refers to the unused portion of its quota at the organization. This reserve tranche represents a potential source of additional liquidity in case of unforeseen balance of payments difficulties.
The Significance of India’s Forex Reserves: A Pillar of Economic Stability
India’s robust forex reserves serve as a linchpin for its economic resilience, offering a plethora of benefits to the nation:
-
External Shock Absorption: Forex reserves act as a buffer against external shocks, such as a sudden decline in exports or a surge in import costs. By utilizing reserves to intervene in the foreign exchange market, the RBI can maintain exchange rate stability and prevent excessive volatility.
-
Facilitate International Payments: Forex reserves provide a source of liquidity for international payments, enabling Indian businesses to settle transactions with foreign entities promptly and efficiently. This smooth flow of payments supports trade and investment activities.
-
Safeguarding Economic Growth: Sufficient forex reserves enhance India’s creditworthiness and attract foreign investments, fostering economic growth and employment generation. A stable reserve position provides a sense of confidence to global investors and reduces the perceived country risk.
-
Preserving Currency Value: By intervening in the foreign exchange market, the RBI can prevent sharp fluctuations in the value of the Indian rupee. Stable currency values promote economic stability and protect domestic consumers from the impact of imported inflation.
Components Of Forex Reserves Of India
Conclusion: India’s Forex Reserves, a Keystone of Economic Well-being
India’s foreign exchange reserves stand as a cornerstone of its economic stability, aiding in the management of external risks, facilitating international transactions, and supporting economic growth. By maintaining adequate forex reserves, the Reserve Bank of India ensures the nation’s resilience against global economic uncertainties and lays the foundation for sustainable prosperity.






