Introduction
Welcome to the dynamic and lucrative world of forex trading, where countless opportunities await astute investors. Foreign exchange (forex) is the buying and selling of currencies on the world’s financial markets, offering the potential for substantial profits and the flexibility to trade from anywhere with an internet connection. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of โบ ร ค เภà¸à¸£à¹Œ forex trading, providing you with the knowledge and strategies to navigate the complexities of this global marketplace.
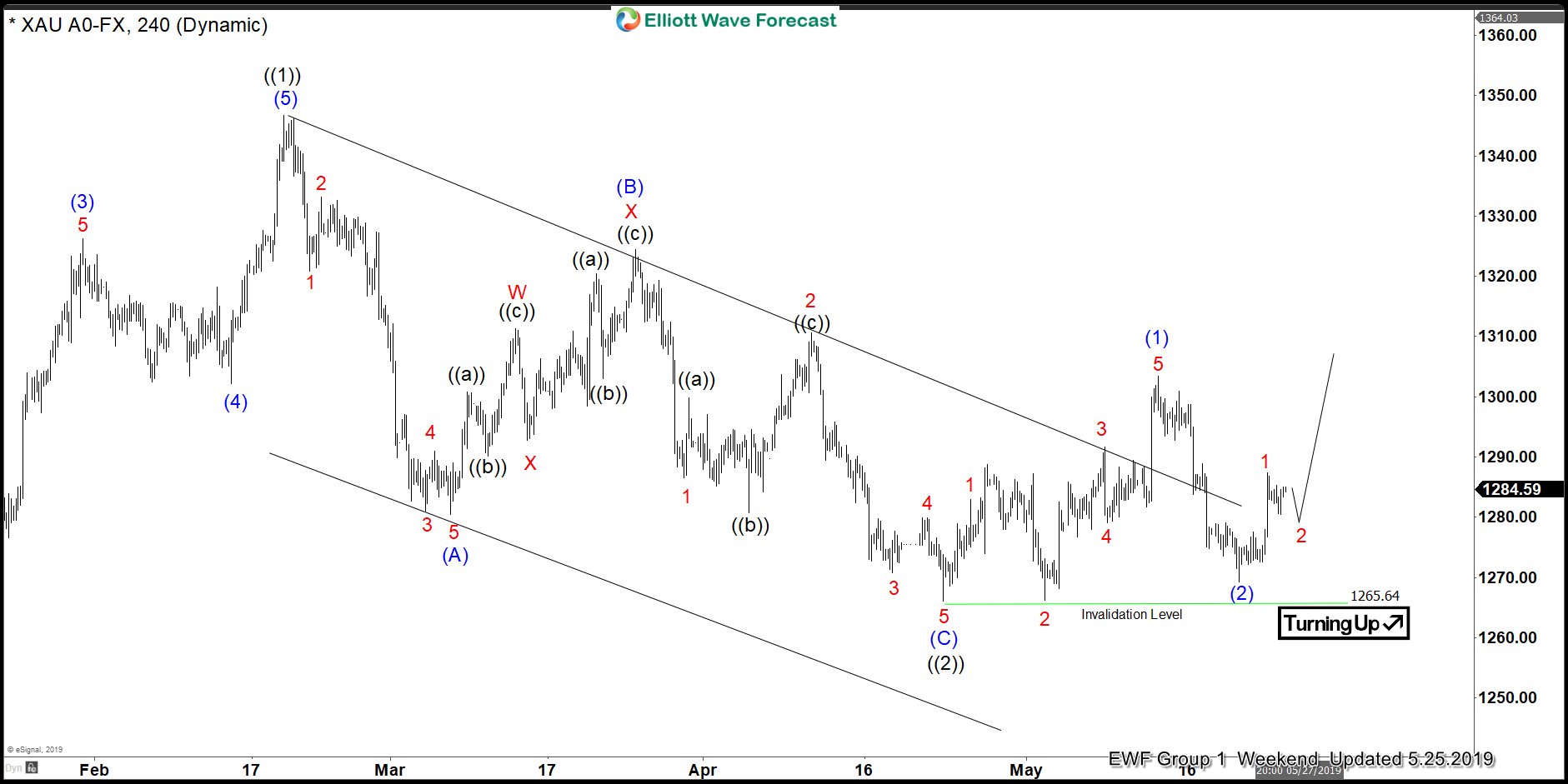
Image: forexsystemaccurate.blogspot.com
Understanding the Forex Market
The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with daily trading volumes exceeding trillions of dollars. Forex trading involves the exchange of one currency for another at agreed-upon exchange rates. Unlike stock markets, which have specific operating hours, the forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, catering to traders from different time zones.
Why Trade Forex?
There are several compelling reasons to consider trading forex:
High Liquidity:
The immense trading volume in the forex market ensures that there are always buyers and sellers willing to trade, making it easy to execute trades quickly and at competitive prices.
Image: clarisights-journal.netlify.app
24/5 Trading:
Unlike other financial markets, the forex market’s round-the-clock operation allows traders to take advantage of market movements at any time that suits them.
Leverage:
Forex brokers often provide traders with leverage, which allows them to control a larger position size with a smaller initial deposit. While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses, so it should be used with caution.
Profit Potential:
Currency fluctuations provide profit-making opportunities for traders who can correctly predict market direction. The vast trading volume and volatility create ample chances for quick profits.
Basic Concepts of Forex Trading
Before entering the forex market, it is essential to understand some fundamental concepts:
Currency Pairs:
Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another, which is represented as a currency pair. For example, the EUR/USD currency pair represents the price of one euro in terms of US dollars. The left-hand currency is known as the base currency, and the right-hand currency is the quote currency.
Pip:
Pip stands for “point in percentage” and represents the smallest unit of price movement in a currency pair. The pip value varies depending on the currency pair, but it is typically the fourth decimal place for most major currency pairs. A 1-pip movement means the exchange rate has changed by one hundredth of one percent.
Spread:
The spread is the difference between the bid price (the price at which you can sell) and the ask price (the price at which you can buy) of a currency pair. The spread represents the broker’s commission for executing the trade.
Trading Strategies and Technical Analysis
Successful forex traders employ various trading strategies and technical analysis tools to predict market movements and make informed decisions. Some popular strategies include:
Trend Following:
Trend following strategies involve identifying the prevailing market trend and trading in line with that trend. Traders use technical indicators such as moving averages and trend lines to determine the trend direction.
Range Trading:
Range trading involves identifying a currency pair that is trading within a defined price range and trading between the support and resistance levels of that range.
À¹‚À¸Š À¸£ À¸„ À¹€À¸À¸À¸£À¹Œ Forex
Scalping:






