Introduction
In the dynamic and often enigmatic world of forex trading, the concept of deviation plays a crucial role in empowering traders to navigate market uncertainties with greater confidence and precision. Deviation, in essence, refers to the variance between the actual value of an asset or indicator and its predicted or expected value. Understanding deviation and its implications is paramount for traders seeking to maximize their trading potential and minimize risks.
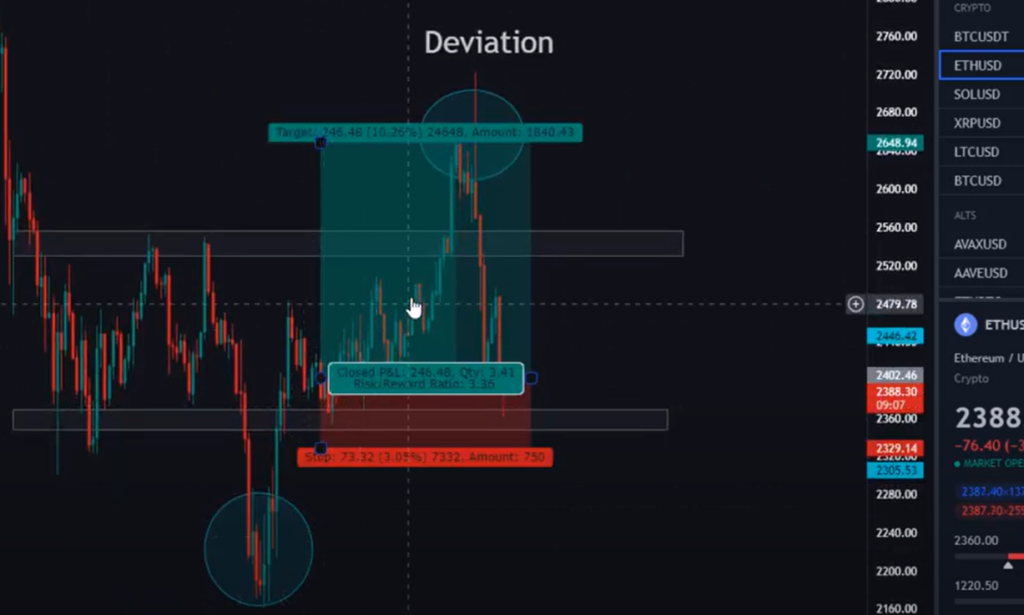
Image: forexprofy.com
Demystifying Deviation in Forex
Deviation in forex can manifest in various forms, measuring the divergence between different price points, indicators, or forecasts. The most common types of deviation include standard deviation, moving average deviation, relative strength index deviation, and Bollinger band deviation. Each type offers valuable insights into market behavior, helping traders identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk exposure effectively.
Standard Deviation: Quantifying Price Volatility
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of price volatility, indicating the extent to which an asset’s price fluctuates around its average value. A higher standard deviation signifies greater price volatility, while a lower standard deviation suggests a more stable price environment. By understanding standard deviation, traders can assess the risk associated with a particular asset and make informed decisions about position sizing and trade management strategies.
Moving Average Deviation: Identifying Trend Reversals
Moving average deviation (MAD) measures the distance between an asset’s price and its moving average, capturing potential trend reversals. A widening MAD typically indicates increased volatility and could signal an impending trend change. Traders can use MAD to identify potential buy or sell opportunities by observing when the price crosses above or below the moving average plus or minus the MAD value.
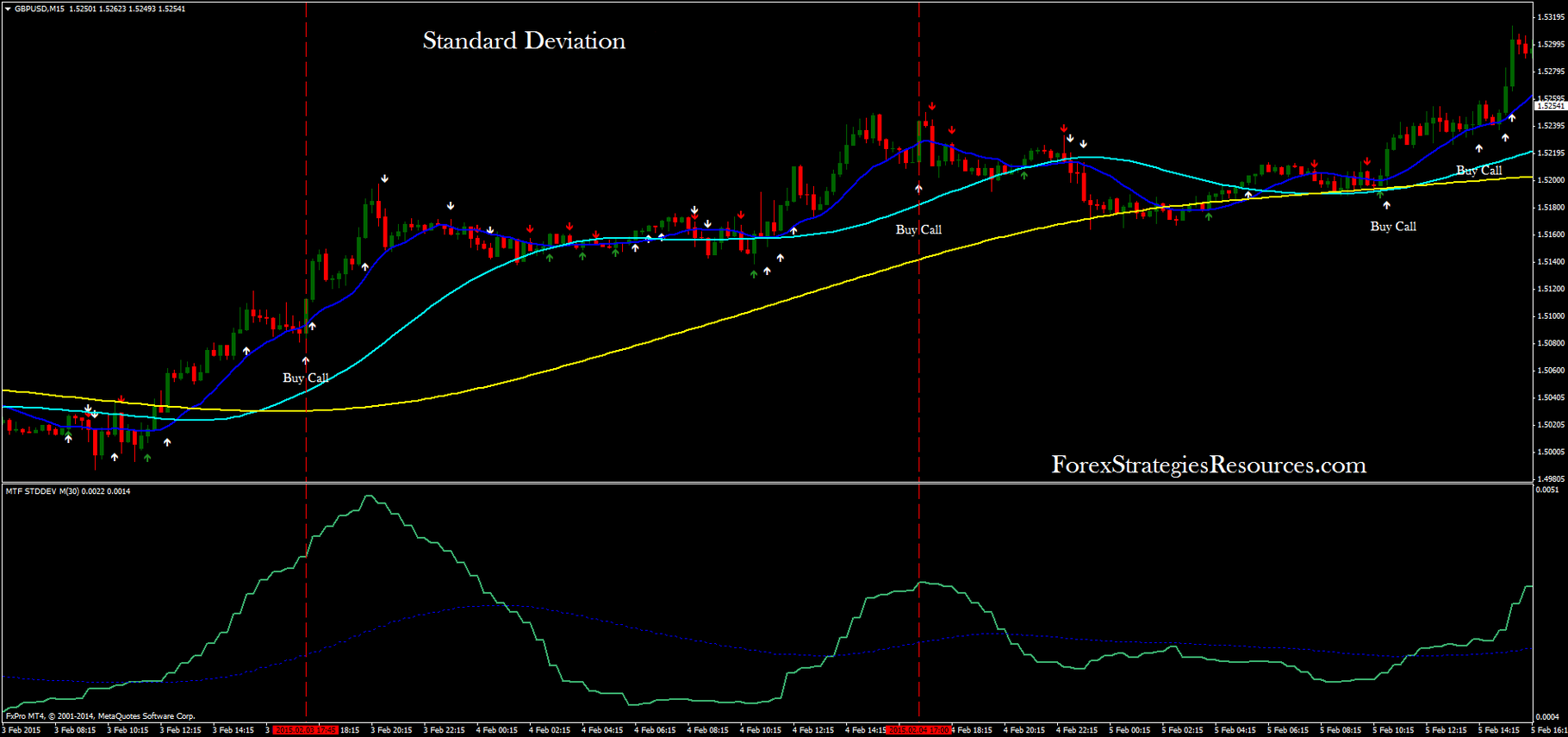
Image: www.forexstrategiesresources.com
Relative Strength Index Deviation: Assessing Momentum and Oversold/Overbought Conditions
The relative strength index (RSI) deviation measures the deviation of the RSI indicator from its neutral value of 50. A positive deviation indicates overbought conditions, while a negative deviation suggests oversold conditions. Traders can use RSI deviation to identify potential buying opportunities in oversold markets and selling opportunities in overbought markets.
Bollinger Band Deviation: Identifying Trend Peaks and Valleys
Bollinger bands are a technical indicator that creates upper and lower bands based on standard deviation calculations. The Bollinger band deviation measures the distance between the asset’s price and the upper or lower Bollinger band. Extreme deviations can indicate potential trend peaks or valleys, providing traders with valuable insights into potential trading reversals.
Expert Insights: Harnessing Deviation for Trading Success
According to Mark Douglas, renowned trading psychologist, “Deviation is the price we pay for freedom in the markets.” By embracing deviation, traders can liberate themselves from rigid trading systems and develop a more flexible and adaptive approach to trading.
Professional trader John Bollinger, creator of the Bollinger bands, emphasizes the importance of understanding deviation: “The greater the price deviation from the moving average, the greater the probability of a reversal.” Traders who master the art of detecting and interpreting deviation can gain a significant advantage in identifying trading opportunities and navigating market volatility.
Actionable Tips: Empowering Traders with Deviation-Based Strategies
-
Incorporate Standard Deviation Calculations: Quantify market volatility by calculating standard deviation to determine the level of risk associated with a particular asset. Adjust position sizing and trade management strategies accordingly.
-
Monitor Moving Average Deviation: Track MAD to identify potential trend reversals. Look for instances when the price crosses above or below the moving average plus or minus the MAD value.
-
Utilize RSI Deviation: Identify overbought or oversold conditions using RSI deviation. Buy when the deviation is negative (oversold) and sell when the deviation is positive (overbought).
-
Employ Bollinger Band Deviation: Determine potential trend peaks or valleys by calculating Bollinger band deviation. Monitor extreme deviations to anticipate trading reversals.
What Is Deviation In Forex
Conclusion
Deviation in forex is an invaluable tool for traders seeking to unravel market uncertainties and make informed decisions. By mastering the concepts of standard deviation, moving average deviation, relative strength index deviation, and Bollinger band deviation, traders can equip themselves with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the dynamic forex landscape effectively. Remember, understanding deviation empowers traders to quantify risk, identify trading opportunities, and ultimately achieve their financial goals.






