The currency market participants (CMP), also known as the interbank or forex market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an estimated daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. Unlike a centralized exchange, the CMP is an over-the-counter (OTC) market, meaning trades are conducted directly between two parties without a central exchange or intermediary.

Image: www.istockphoto.com
The CMP plays a vital role in the global economy. It facilitates international trade, investment, and tourism by allowing businesses and individuals to exchange currencies. Moreover, it provides a platform for speculators to profit from currency fluctuations.
Sub-Interbank Market
The sub-interbank market refers to the smaller segment of the CMP that involves transactions between banks and non-bank financial institutions, such as hedge funds, brokerages, and other large institutional investors. While the interbank market primarily serves inter-bank liquidity, the sub-interbank market caters to the currency exchange needs of other financial market participants.
The participants in the sub-interbank market often have different risk appetites and trading strategies compared to banks in the interbank market. Hedge funds, for example, may engage in speculative trading, while asset managers may focus on currency hedging for investment portfolios.
Definition, History, and Meaning of CMP
The CMP is a global network of banks, brokers, and other financial institutions that facilitate the exchange of currencies. It is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with a daily trading volume that exceeds $5 trillion. The CMP operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and it is accessible to individuals, businesses, and institutions from all over the world.
The history of the CMP can be traced back to the early days of international trade. In the past, merchants would exchange currencies to facilitate transactions between countries. As global trade grew, the need for a more organized and efficient system for exchanging currencies became apparent.
The establishment of the modern CMP occurred in the early 20th century. In 1971, the US dollar was delinked from the gold standard, which led to the creation of a floating exchange rate system. This system allowed currencies to fluctuate freely based on supply and demand, and it created the conditions for the modern CMP to develop.
The CMP is a complex and dynamic market that is constantly evolving. However, its fundamental purpose remains the same: to facilitate the exchange of currencies between market participants.
The Importance of CMP
The CMP is essential for the smooth functioning of the global economy. It enables businesses and individuals to exchange currencies for a variety of purposes, including:
The CMP is an essential component of the global financial system. It provides a platform for market participants to exchange currencies and is essential for facilitating international trade and investment.
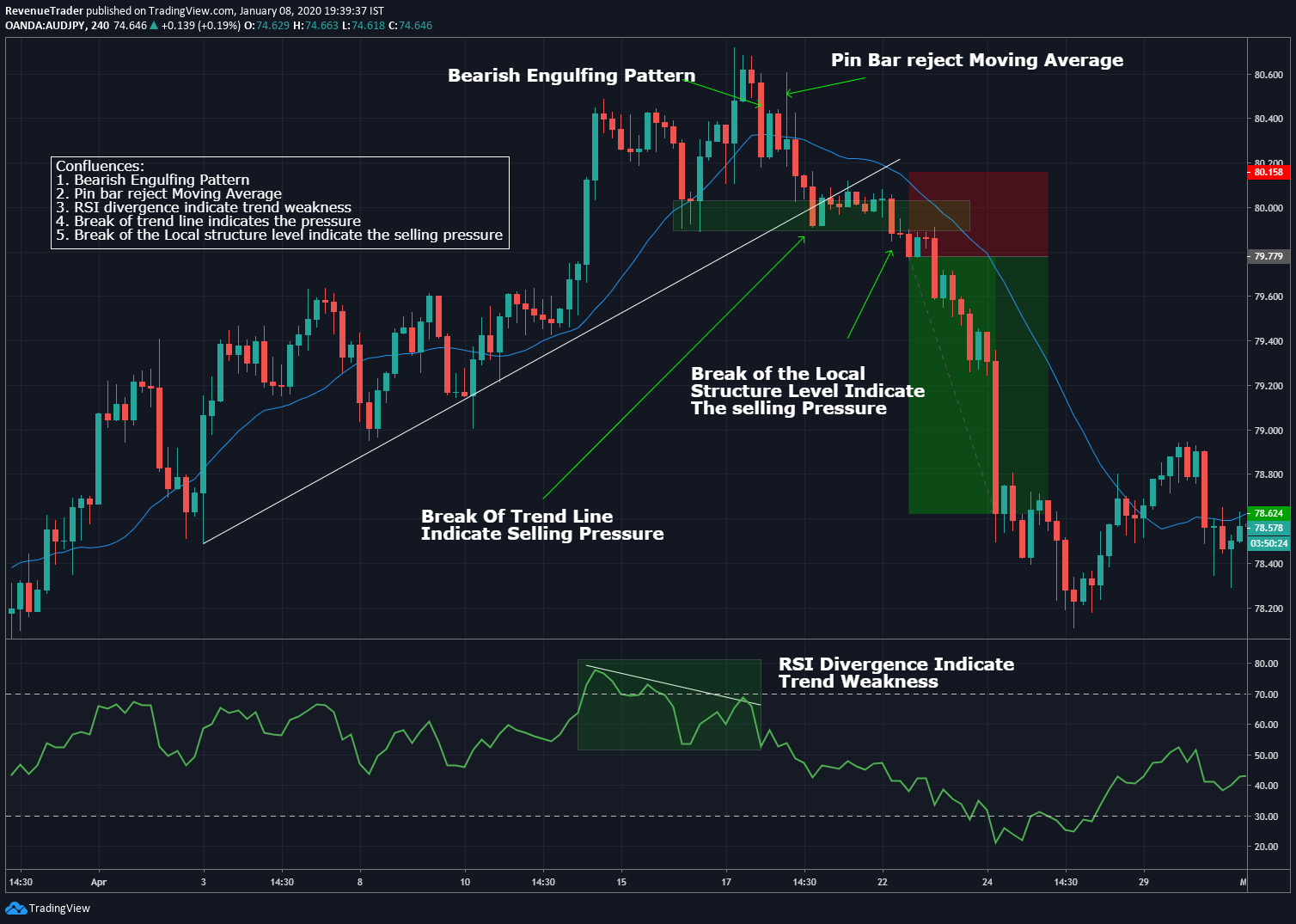
Image: traderevenuepro.com
Tips and Expert Advice
Here are some tips and expert advice for trading in the CMP:
By following the advice of a professional broker, you are increasing your chances of success in the CMP.
FAQs about CMP
- What is the difference between the interbank market and the retail forex market?
- The interbank market is the market where banks trade currencies with each other. The retail forex market is the market where individual traders trade currencies with each other through a broker.
- What are the advantages of trading in the CMP?
- The CMP offers the following advantages:
- High liquidity: The CMP is the most liquid financial market in the world, which means that it is easy to buy and sell currencies.
- Low transaction costs: The cost of trading in the CMP is relatively low compared to other financial markets.
- 24-hour trading: The CMP is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, which means that you can trade whenever you want.
- Access to a variety of currencies: The CMP offers access to a wide range of currencies, including major currencies like the US dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen, as well as minor currencies like the Thai baht and the Hungarian forint.
- What are the risks of trading in the CMP?
- There are a number of risks associated with trading in the CMP, including:
- Currency risk: The value of currencies can fluctuate rapidly, which means that you could lose money if the currency you are trading against moves in an unfavorable direction.
- Leverage risk: Leverage is a tool that can be used to increase your potential profits, but it can also increase your potential losses.
- Liquidity risk: The CMP is a liquid market, but there are times when it can become illiquid, which means that it may be difficult to buy or sell currencies at a fair price.
What Is Cmp In Forex
Conclusion
The CMP is a complex and dynamic market that plays a vital role in the global economy. It provides a platform for businesses and individuals to exchange currencies for various purposes. Understanding the CMP is essential for anyone who wants to participate in the global financial markets.
If you are interested in trading in the CMP, I recommend that you do your research and learn as much as you can about the market. I also recommend that you work with a reputable broker who can provide you with the support and guidance you need to succeed.






