India’s foreign exchange reserves, a crucial indicator of the country’s economic stability, have been a topic of much debate and speculation in recent times. These reserves, which primarily comprise foreign currencies like the US dollar, euro, and British pound, play a pivotal role in managing the country’s external liabilities, maintaining exchange rate stability, and ensuring access to foreign goods and services. In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of India’s forex reserves, examining their buildup, composition, and significance, while also exploring concerns related to their sustainability and implications for the Indian economy.
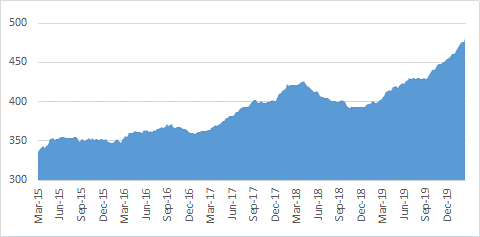
Image: investmentcorner.bajajallianzlife.com
Understanding India’s Forex Reserves: A Historical Perspective
India’s forex reserves underwent a significant transformation in the post-liberalization era, beginning in the 1990s. Prior to this, the country’s reserves were relatively modest, primarily due to restrictive trade policies and foreign exchange regulations. However, following the implementation of economic reforms, there was a concerted effort to increase forex reserves to protect the country from external shocks and bolster its international standing. This proactive approach led to a substantial accumulation of reserves, reaching record levels in recent years.
Composition and Management of India’s Forex Assets
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), India’s central bank, is responsible for managing the country’s forex reserves. These reserves are primarily held in the form of US dollars, but they also include other currencies such as the euro, British pound, yen, and Canadian dollar. The RBI actively manages the reserves through a combination of investments in foreign government securities, deposits with foreign central banks, and special drawing rights (SDRs) issued by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Benefits and Significance of Ample Forex Reserves
Robust forex reserves provide India with several advantages that contribute to its economic resilience and stability. Firstly, these reserves ensure India’s ability to meet its external obligations, such as repaying foreign debt and paying for essential imports. They also serve as a buffer against external shocks like sudden capital outflows or currency fluctuations, thus preventing sharp depreciations in the value of the Indian rupee. Furthermore, ample forex reserves enhance India’s credibility among foreign investors and rating agencies, facilitating access to foreign capital and favorable ratings.

Image: economictimes.indiatimes.com
Concerns over Forex Reserve Sustainability
While India’s forex reserves have been a source of strength for the economy, some experts have raised concerns about their sustainability. The recent depletion of reserves, coupled with a widening trade deficit, has led some analysts to question whether India’s forex reserve buildup can be maintained in the long run. Moreover, concerns have been raised about the concentration of reserves in a relatively small number of currencies, particularly the US dollar, which exposes India to exchange rate risks.
Implications for the Indian Economy
The sustainability of India’s forex reserves and their implications for the Indian economy are multifaceted. A sustained decline in reserves could erode confidence in the economy, making it more difficult for India to attract foreign capital and leading to potential pressure on the rupee. On the other hand, a strong and growing forex reserve position can provide a cushion against external shocks, allowing the government and central bank greater flexibility in managing economic policies.
India Forex Reserves And Debt
Conclusion: Navigating the Future
India’s forex reserves have played a critical role in supporting the country’s economic growth and stability over the past decades. However, the recent challenges and concerns surrounding their sustainability necessitate careful consideration and prudent management. The Indian government and the RBI will need to strike a delicate balance, ensuring adequate reserves to meet external obligations and mitigate risks while addressing concerns about sustainability. By diversifying the composition of reserves, strengthening the export sector, and managing external debt responsibly, India can continue to leverage its forex reserves as an asset for economic resilience and long-term growth.






