Introduction
In the bustling world of forex trading, leverage plays a pivotal role in amplifying profit potential. Understanding how to calculate leverage is essential for traders to harness its power while managing associated risks. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of leverage, its formula, implications, and prudent usage for successful forex trading.
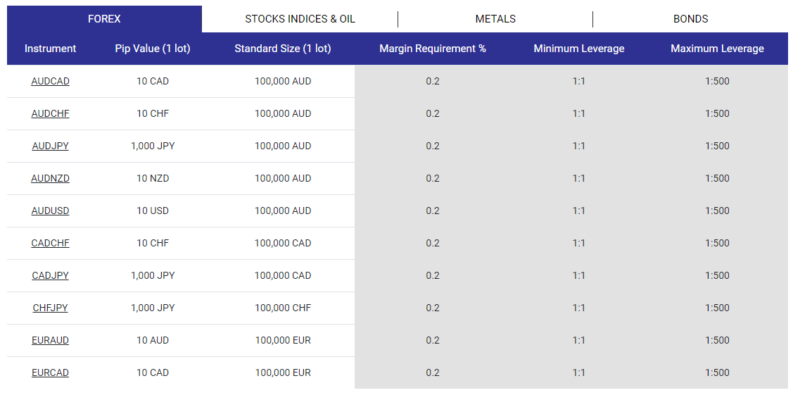
Image: www.asktraders.com
Understanding Forex Leverage
Forex leverage enables traders to control a larger trading position than their account balance would allow. It acts as a loan from brokers, allowing traders to amplify their profits and losses. The leverage ratio represents the multiple at which traders can leverage their trades. For instance, a leverage of 1:100 implies that for every $1 in their account, traders can control a $100 position.
Calculating Leverage: A Simple Formula
Calculating leverage is straightforward, requiring only the division of total position size by the account balance. The formula is:
Leverage = Total Position Size / Account Balance
For example, if a trader buys a currency pair worth $100,000 with an account balance of $1,000, the leverage would be:
Leverage = $100,000 / $1,000 = 1:100
Implication of Leverage: High Profit, High Risk
Leverage offers the potential for significant profit amplification. With higher leverage, smaller price movements can yield substantial gains. However, the double-edged sword of leverage poses a parallel risk. Losses are also amplified, making it crucial to exercise caution when selecting leverage levels.
Margin calls occur when account balances dip below a certain threshold due to losses. In such scenarios, brokers may force traders to close positions or contribute additional funds, potentially leading to significant financial setbacks. It’s imperative to understand and carefully manage risk tolerance before engaging in leveraged trading.
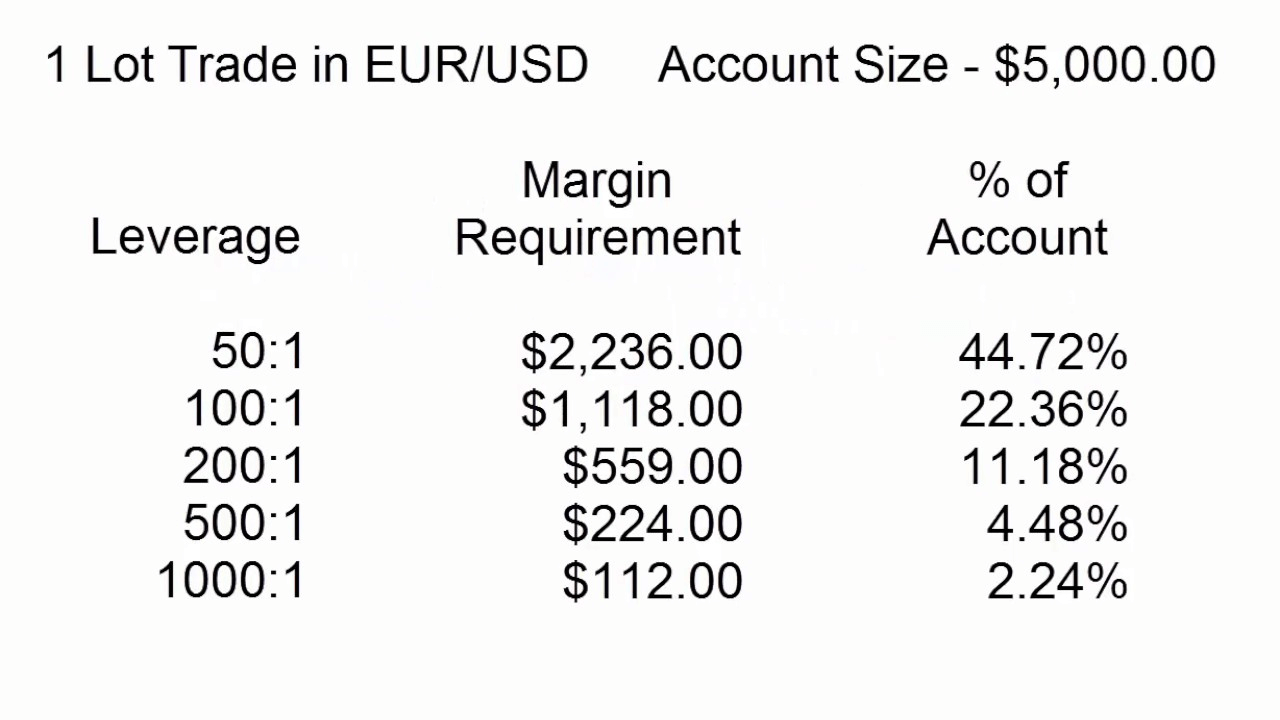
Image: fxtechlab.com
Selecting Appropriate Leverage Levels
Optimal leverage levels are highly subjective, influenced by individual risk tolerance, trading experience, and market conditions. Forex beginners are generally advised to adopt conservative leverage ratios between 1:10 and 1:20. Experienced traders may venture into higher leverage, up to 1:50 or even 1:100, but must possess the discipline and risk management skills to mitigate potential losses.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Leverage
Several factors need consideration when selecting leverage levels:
- Risk Appetite: The higher the leverage, the more volatile the potential losses; assess your tolerance for risk before deciding.
- Market Volatility: In volatile markets, excessive leverage can lead to rapid account depletion due to sudden price swings.
- Trading Strategy: Scalping and short-term trading often necessitate higher leverage to capitalize on small price movements, while long-term investors can opt for lower leverage.
- Account Balance: Leveraging should be proportionate to your account size; higher leverage with a small balance can lead to significant risk exposure.
How To Calculate Leverage In Forex
Conclusion
Mastering the art of forex leverage calculation is a cornerstone of successful trading. By understanding its formula, appreciating its implications, and making prudent leverage selections, traders can harness its power while effectively managing associated risks. Remember, leverage is a double-edged sword; while it amplifies profit potential, it also intensifies potential losses. Embrace a balanced approach, considering your risk appetite, market dynamics, and trading strategy to maximize your forex trading success.






