Introduction
The world of finance has become increasingly interconnected, with opportunities for investment and economic growth spanning borders. Forex trading, the exchange of currencies between different countries, has emerged as a prominent avenue for traders to capitalize on global market movements. In India, forex trading presents a unique landscape, offering its citizens avenues to participate in the lucrative currency exchange arena. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of how forex trading operates within the Indian context, empowering aspiring traders with the knowledge and strategies to navigate this dynamic market.
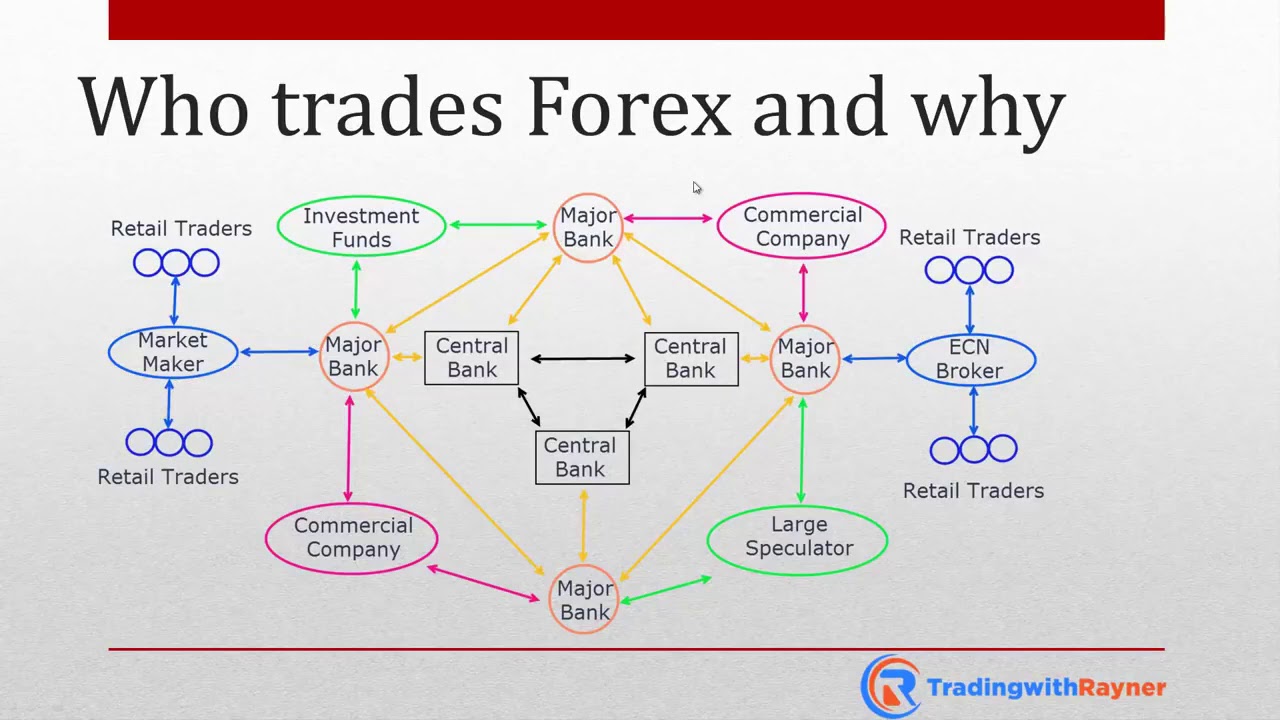
Image: www.youtube.com
Understanding Forex Trading in India
Foreign exchange trading (forex) is the buying and selling of currencies with the aim of making a profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. In India, forex trading is primarily regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which governs the licensing and oversight of Authorized Dealer (AD) banks that facilitate forex transactions. AD banks, such as Kotak Mahindra Bank, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank, provide a secure platform for traders to access the global forex market.
Eligibility for Forex Trading in India
Indian residents who meet specific eligibility criteria can engage in forex trading. These criteria include:
- Being at least 18 years old
- Having a valid PAN card and bank account
- Maintaining a minimum account balance as specified by the AD bank
- Passing a forex trading proficiency test conducted by designated exchanges [For Indian citizen & PIO Card Holder only]
Types of Forex Orders
When trading forex, traders can execute different types of orders, each with its unique set of characteristics:
- Market Order: This order executes immediately at the current market price, ensuring quick execution but potentially limiting profit potential due to slippage.
- Limit Order: With a limit order, traders specify a price at which they would like to buy or sell a currency. The order is executed only when market conditions match the specified price, offering greater control over transaction pricing.
- Stop Order: A stop order is used to limit losses or initiate a trade when a specific price level is reached. A sell stop order is triggered when a currency pair falls below a certain level, while a buy stop order executes when the pair rises above a predetermined threshold.
- Stop-Limit Order: Combining elements of stop and limit orders, a stop-limit order places a limit order only after a specific market price level has been breached, providing additional protection against adverse price movements.
Image: www.pelajaran.guru
Trading Strategies
Successful forex traders employ a variety of strategies to enhance their profitability. Some common approaches include:
- Scalping: Scalping involves entering and exiting trades rapidly, taking advantage of small price fluctuations throughout the trading day. This strategy requires sharp execution and risk management skills.
- Day Trading: Day traders hold trades for a single trading session, closing all open positions before the market closes, aiming to capture intraday market movements.
- Swing Trading: Swing trading encompasses holding positions for several days or weeks, focusing on identifying and capitalizing on short-term to mid-term price trends.
- Position Trading: Position traders maintain trades for extended periods, sometimes months or years, based on long-term market outlooks and fundamental analysis.
Tips for Forex Trading in India
- Educate Yourself: Thoroughly understand the concepts and risks associated with forex trading before venturing into the market. Utilize resources such as online courses, webinars, and books to enhance your knowledge.
- Practice with a Demo Account: Open a demo account with an AD bank or online forex broker to familiarize yourself with trading platforms and strategies without risking real capital.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Establish a well-defined trading strategy that outlines your risk tolerance, trading methodology, and money management practices.
- Manage Your Risk Effectively: Implement sound risk management strategies such as stop-loss orders and position sizing to limit potential losses.
- Monitor Market Trends: Stay informed about global economic news and events that may impact forex markets, including interest rate decisions, economic data releases, and political developments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is forex trading in India illegal?
A: No, forex trading is not illegal in India. It is regulated by the RBI, which provides guidelines for authorized dealers to facilitate forex transactions.
Q: How much capital is required to start forex trading in India?
A: AD banks typically set minimum account balance requirements, which vary depending on the bank and trader’s risk profile. Some brokers may offer accounts with lower minimum deposits.
Q: What are the tax implications of forex trading in India?
A: Profits earned from forex trading are subject to taxation at the prevailing income tax rates in India. Income from forex trading is considered business income and is taxed under the relevant tax slabs.
How Does Forex Trading Work In India
Conclusion
Forex trading presents a dynamic and rewarding opportunity for Indian traders to engage in the global currency market. By understanding the regulations, eligible criteria, types of orders, trading strategies, and industry best practices outlined in this article, aspiring traders can equip themselves with the knowledge and skills to embark on their forex trading journey with confidence. Whether you seek short-term gains through scalping or long-term investment potential through position trading, the world of forex offers boundless avenues for growth and prosperity for those who approach it with knowledge, discipline, and a commitment to continuous learning.
As you explore the world of forex trading in India, remember the importance of ongoing education, prudent risk management, and a strategic approach. By harnessing the insights and strategies presented within this guide, you can successfully navigate the complexities of the market and unlock the opportunities it holds.






